21st Century Learning

Technology
Real-time collaboration
21st Century Digital Citizenship
Effective use of technology
Cultural awareness
Media Fluency
Information fluency
Cultural Awareness
Quick feedback
Game creation tools
Concept mind map making
Productive Instructional Strategies
Conceptual Understanding & Motivation

Project or Problem-based learning

Inquiry-based Learning

Constructivism

Science Technology Society Environment (STSE)
Student-centered instruction
1. Building on & Expanding Student's Prior Knowledge & Experiences
(i) Teaching Students within the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
(ii) Creating a rich environment
2. Personalized lessons
3. Collaborative learning
4. Cognitive Supports
(i) Elaboration - Summarizing and paraphrasing
(ii) Outlining
(iii) Practice Problem solving & critical thinking
(iv) Teach note taking skills
(v) Provide visual cues & props
(vi) Chunk information
(vii) Songs, rhymes or rhythms
(viii) Rehearsals & role-playing
(ix) Acronyms
(x) Peer tutor
(xi) Graphic Organizers
(xii) Scaffolding
(xiii) Think-pair share
(xiv) Learning groups
Teaching How to Students to Learn
1. Metacognitive strategies
(i) Organizational Tools

(a) Checklists
(b) Rubrics

(c) Achievement Charts

(d) Consistent rules & polices
(e) Timelines/Schedules
(f) Graphic Organizers
(g) Create objectives & Goals

(ii) Goal Setting
(iii) Lecture Wrapper
(iv) Think-Alouds
(a) Reading Comprehension

Guided Reading Stratgies
(b) Problem-solving

(c) Role-playing
2. Diagnostic Assesment
3. Formative feedback
(i) Practice
(ii) Revision

(iii) Peer Editing
(iv) Self-evaluation/peer-evaluation

4. Modeling & Coaching
(i) Planning
(ii) Monitoring
(iii) Evaluating
5. Guided practice
6. Independent Practice
7. Self-regulate
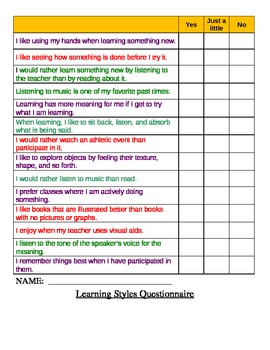
Learning Style Inventory
Assessing Students
Clear & Transparent Goals/Objectives
Relevant & Engaging Tasks
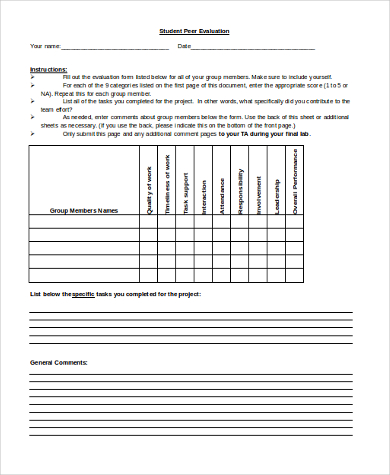
Self-evaluation & Peer Evaluation
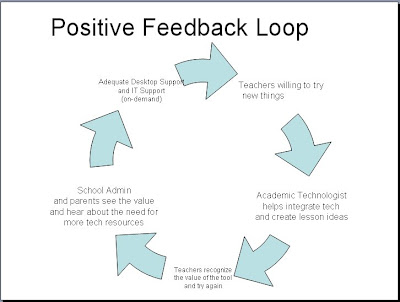
Appropriate/constructive Feedback
Timely Feedback
Diagnostic Assessment
Formative Assessment
Teacher observations
Self-evaluation
Peer evaluation
Journals
Quiz
Classroom discussions
Learning/response logs
Conferencing & reviews
Concept maps/graphic organizers
Summative Assessment
Portfolios
Labs
Assignments
Projects
Quiz/test
Presentation
Performance
Article analysis
Concept maps
Communication
Collaboration
Supportive Environment
1. Classroom Learning Communities

Consistent routines & Policies

Team-building & relationship building exercises
Trust building
Leadership
Creative thinking
Cultural awareness
2. Connections among staff & families

Relational trust
Staff collaboration
Staff Competence
Voluntary Associations
Regular parent meetings & visits
Authentic Family Engagement
3. Structures for effective caring
Small class sizes
Looping
Block scheduling
Team teaching
Social and Emotional Development
Systems of Support
1.
Knowledge of Childhood Development
Subtopic
Subtopic
Collaborative Communities
Teaching Teams
Advisory systems
Create a professional learning community outside of school

Multiple Intelligences
High Order thinking skills (HOTS)