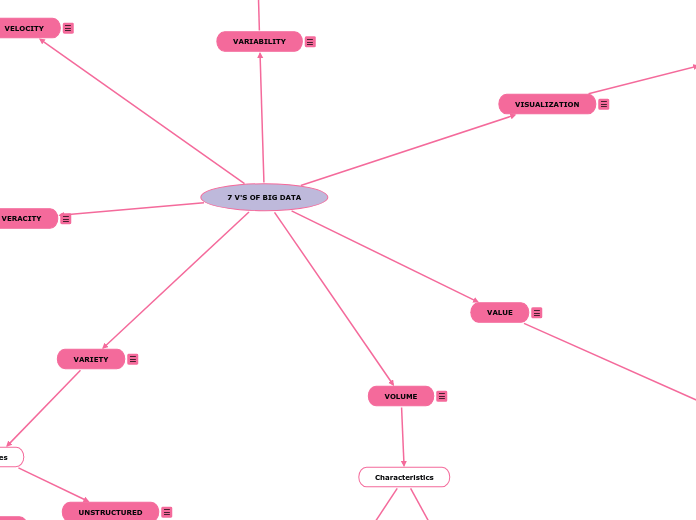
7 V'S OF BIG DATA
VELOCITY
Characteristics
REAL TIME ANALYSIS
FAST PROCESSING
VERACITY
Characteristics
PRECISION
CONSISTENCY
RELIABILITY
VARIETY
Types
STRUCTURED
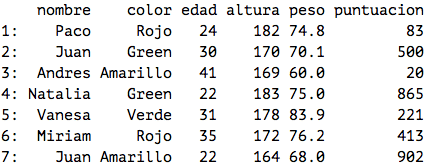
Example : filled information tables
UNSTRUCTURED
Example : media files
SEMI STRUCTURED
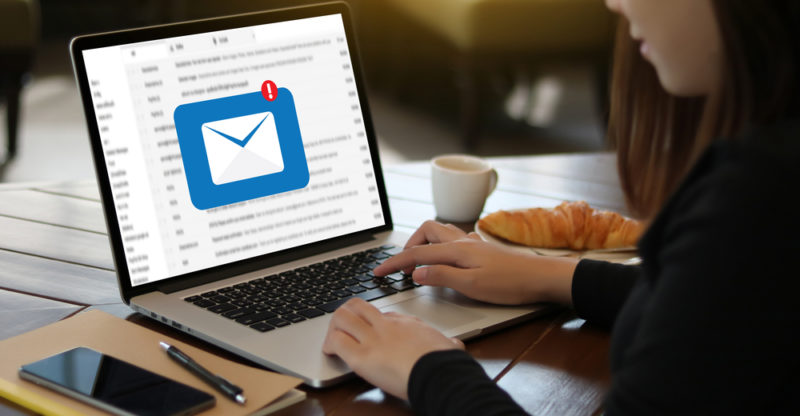
Example : a e-mail
VISUALIZATION
Items

Graphs
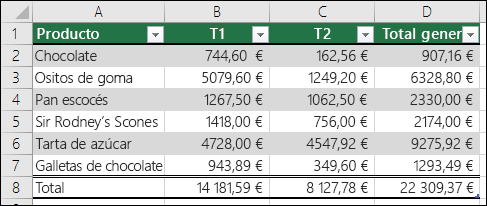
Tables
Dashboards

Diagrams
VALUE
Objetives
IDENTIFY OPPORTUNITIES
STRATEGIC DECISIONS
BUSSINES IMPACT
UTILITY
VARIABILITY
Characteristics
CONSTANT CHANGE
TEMPORARY VARIABILITY
DIVERSITY OF DATA
FLUCTUATION
VOLUME
Characteristics
LARGE TO PROCESS
MASSIVE INFORMATION

Example: All credit card transaction on a day