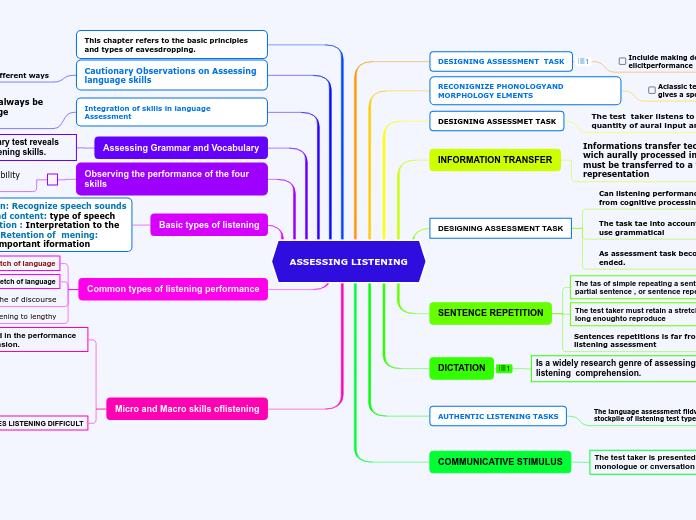
ASSESSING LISTENING
DESIGNING ASSESSMENT TASK
Incluide making decisions about how you will elicitperformance
RECONIGNIZE PHONOLOGYAND MORPHOLOGY ELMENTS
Aclassic test task toasses this recognition gives a spoen stimulus and aks test
DESIGNING ASSESSMET TASK
The test taker listens to a limited quantity of aural input and must
LISTENING CLOZE
Require the test taker to listen to a story
INFORMATION TRANSFER
Informations transfer technique in wich aurally processed infromation must be transferred to a visual representation
iITEMS
Are somentimes efficient rubricsfor assesssig certaiin select infromation
DESIGNING ASSESSMENT TASK
Can listening performance be distinguished from cognitive processing factors
The task tae into account test tkers abilityto use grammatical
As assessment task become more open ended.
SENTENCE REPETITION
The tas of simple repeating a sentence or a partial sentence , or sentence repetition
The test taker must retain a stretch of language long enoughto reproduce
Sentences repetitions is far froma flawless listening assessment
DICTATION
Is a widely research genre of assessing listening comprehension.
This chapter refers to the basic principles and types of eavesdropping.
AUTHENTIC LISTENING TASKS
The language assessment fildwould have a stockpile of listening test types that are cognitively
NOTETAKING
In the academic world ,classroom lectures by professors are commom features
EDITING Another authentic task provides both a written and a spoken stimulus and requires
Cautionary Observations on Assessing language skills
Any skill can be evaluated in different ways
COMMUNICATIVE STIMULUS
The test taker is presented with a stimulu monologue or cnversation
Integration of skills in language Assessment
Integration of skills should always be a priority to achieve language authenticity.
Assessing Grammar and Vocabulary
Any grammar or vocabulary test reveals two or more separate listening skills.
Observing the performance of the four skills
First principle for assessing - reliability
Second principle - trust
Basic types of listening
Recognition: Recognize speech sounds Context and content: type of speech Interpretation : Interpretation to the message . Retention of mening: retaining important iformation
Common types of listening performance
Intensive: Larger stretch of language
Responsive: Short stretch of language
Selective: Processing streche of discourse
Extensive: Rnages from listening to lengthy
Micro and Macro skills oflistening
Micro and Macro implied in the performance of listening comprenhension.
WHAT MAKES LISTENING DIFFICULT
CLUSTERING Appropriate chunks of language
PERFORMANCE VARIABLES Being able to weed out hesitations
REDUNDANCY Reconigniza the kinds of repetitions, rephrasing
REDUCE FORMS Reduce the forms that may not have been a para of english