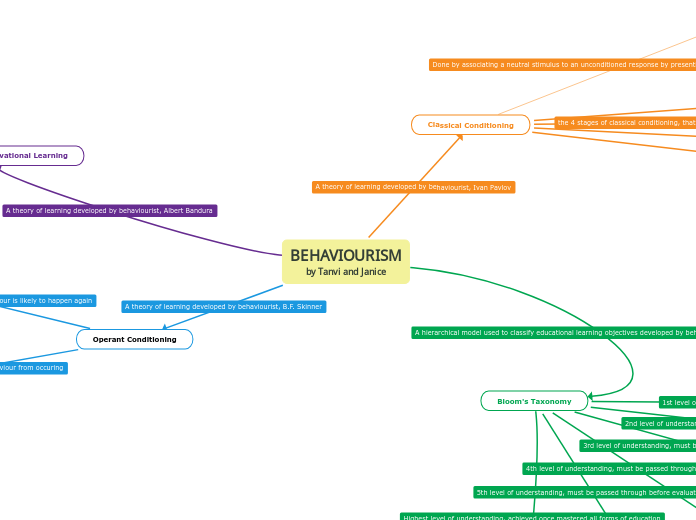
the 4 stages of classical conditioning, that is not in any particular order
Done by associating a neutral stimulus to an unconditioned response by presenting it with an unconditioned stimulus
Highest level of understanding, achieved once mastered all forms of education
5th level of understanding, must be passed through before evaluating
4th level of understanding, must be passed through before creating
3rd level of understanding, must be passed through before analyzing
2nd level of understanding, must be passed through before applying
1st level of understanding - everyone starts here
Last requirement needed where the model is reinforced to enhance the effects of observational learning
Third requirement needed where learner must have skill and practice to be able to replicate
Second requirement needed is for model to provide clarity and meaning to learner
First requirement needed is to gain attention of learner
Adds an adverse stimuli in response to observed behaviour
Takes away something desirable in response to observed behaviour
Takes away something negative after an observed behaviour
Adds something positive to an observed behaviour
A consequence that decreases behaviour from occuring
Strengthens a particular behaviour; behaviour is likely to happen again
A theory of learning developed by behaviourist, Ivan Pavlov
A hierarchical model used to classify educational learning objectives developed by behaviourist, Benjamin Bloom
A theory of learning developed by behaviourist, Albert Bandura
A theory of learning developed by behaviourist, B.F. Skinner