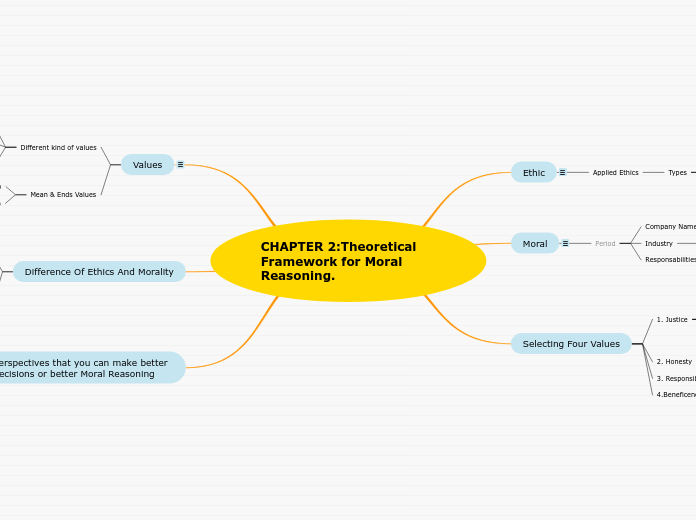
CHAPTER 2:Theoretical Framework for Moral Reasoning.
Ethic
Applied Ethics
Types
1. Educational practice
aims to accelerate the awareness process
2.Political practice
seeks to establish optimum conditions
3.Philosophical practice
aims to develop systematic, creative criticism
Moral
Period
Company Name
Company Name
Industry
Industry
Responsabilities
Responsability
Selecting Four Values
1. Justice
Distributive
Procedural
Retributive
Compensatory
2. Honesty
3. Responsibility
4.Beneficence
Subtopic
Values
Different kind of values
1.Moral Values
Values you hold
2.Aesthetic Values
standards of beauty
3.Performance Values
Benchmarks you set
Mean & Ends Values
1.Instrumental Values (the means)
Objectives used to reach goals
2.Intrinsic Values (the end)
Personal happiness, a comfortable life
Difference Of Ethics And Morality
Ethics
ethics dictate the working of a social system
relates to the philosophy behind a moral outcome
refers to understanding and adopting moral values within the home or workplace that should be defined.
Morality
our character for what is 'right' and 'wrong‘
the moral outcome of a specific situation.
Perspectives that you can make better decisions or better Moral Reasoning
1. Impartiality (fair)
Humans tend to seek own personal pleasure since our system are bombarded with intuition, emotion and others.
2. Consistent
To reason morally, we must be logical
3. Reflection
Reflective thinking is exercising careful judgment in all moral values