Controlling
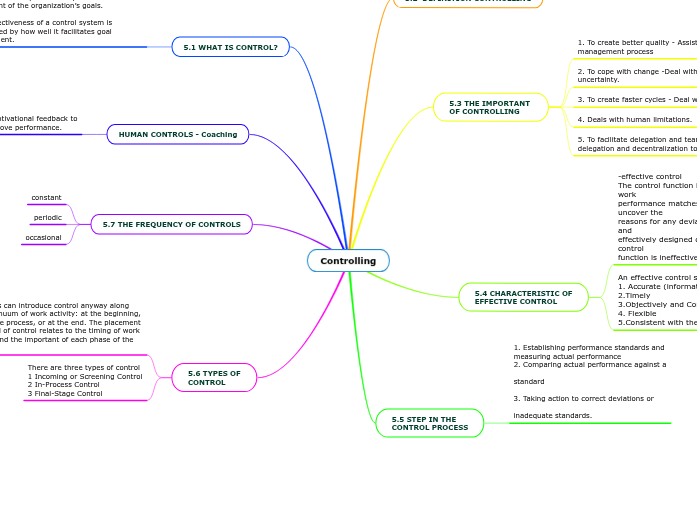
5.2 DEFINITION CONTROLLING
“ The control function is designed primarily to insured that
performance is on schedule according to a plan.”
Bridges & Roquemore, 1993
“Controlling is defined as a process to assure that actual
activities conform to planned activities.”
Stoner, Freeman and Gilbert, 1995
“Monitoring the performance of the organization,
identifying deviations between planned and actual result,
and taking corrective action when necessary.”
Lewis, Goodman & Fandt, 2001
“ Controlling as process of monitoring performance and
taking action to ensure desired result.”
Schermerhorn,1997
5.3 THE IMPORTANT
OF CONTROLLING
1. To create better quality - Assist the management process
2. To cope with change -Deal with change or uncertainty.
3. To create faster cycles - Deal with complexity.
4. Deals with human limitations.
5. To facilitate delegation and teamwork - Help
delegation and decentralization to run smoothly.
5.4 CHARACTERISTIC OF
EFFECTIVE CONTROL
-effective control
The control function is essential to insure that work
performance matches the standards and to uncover the
reasons for any deviations. Without planning and
effectively designed control programs, the control
function is ineffective.
An effective control systems
1. Accurate (information)
2.Timely
3.Objectively and Comprehensive.
4. Flexible
5.Consistent with the organization structure.
5.5 STEP IN THE
CONTROL PROCESS
1. Establishing performance standards and
measuring actual performance
2. Comparing actual performance against a
standard
3. Taking action to correct deviations or
inadequate standards.
5.1 WHAT IS CONTROL?
Controlling
- The process of monitoring activities to ensure that they are being accomplished as planned and of
correcting any significant differences.
- An effective control system ensures that activities are completed in ways that lead to the attainment of the organization’s goals.
- The effectiveness of a control system is determined by how well it facilitates goal achievement.
HUMAN CONTROLS - Coaching
Coaching gives motivational feedback to
maintain and improve performance.
5.7 THE FREQUENCY OF CONTROLS
constant
periodic
occasional
5.6 TYPES OF CONTROL
Managers can introduce control anyway along the continuum of work activity: at the beginning, during the process, or at the end. The placement of control of control relates to the timing of work activity and the important of each phase of the work.
There are three types of control
1 Incoming or Screening Control
2 In-Process Control
3 Final-Stage Control