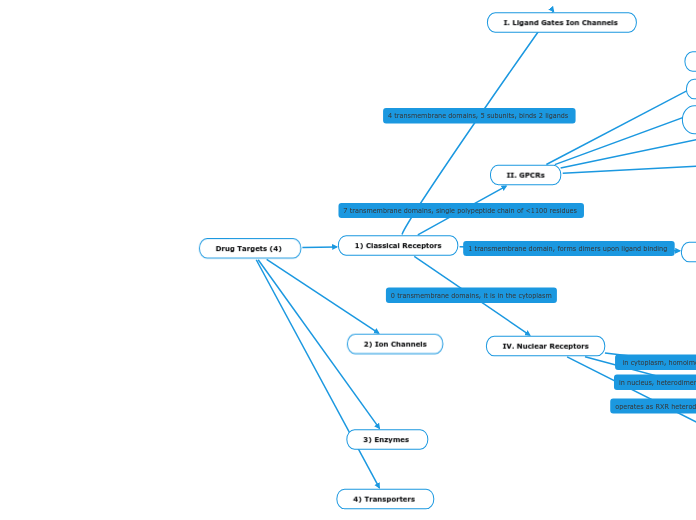
Drug Targets (4)
1) Classical Receptors
I. Ligand Gates Ion Channels
II. GPCRs
a. Rhodopsin Family
b. Secretin/Glucagon Family
c. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor/ Ca Sensor Family
Isoforms of G protein
G alpha s
Upon ligand binding, 'G alpha s' protein dissociates from complex and GDP-> GTP. Activates AC. AC converts ATP to cAMP which goes on to activate PKA.
G alpha i
Upon ligand binding, 'G alpha I' protein dissociates from complex and GDP -> GTP. The protein then inhibits AC so that no cAMP is produced, and thus PKA remains inactive.
G q
Upon ligand binding, 'G alpha Q' dissociates and GDP-> GTP. Activates Phospholipase which then converts PIP3 (in membrane) to IP3 and DAG. DAG activates PKC which goes on to phosphorylate substrates. IP3 travels across the cytosol to the ER where it binds to Ca2+ channels to allow for the outpour of Ca2+ into the cytosol.
IV. Nuclear Receptors
CLASS 1
Hybrid Class
CLASS 2
III. Kinase-Linked Receptors
RTKs
-receptors for growth factors like EGF, NGF and toll-like receptors
Serine/Threonine Kinases
-Transforming Growth Factor Receptor
Cytokine Receptors
-Associate with JAK