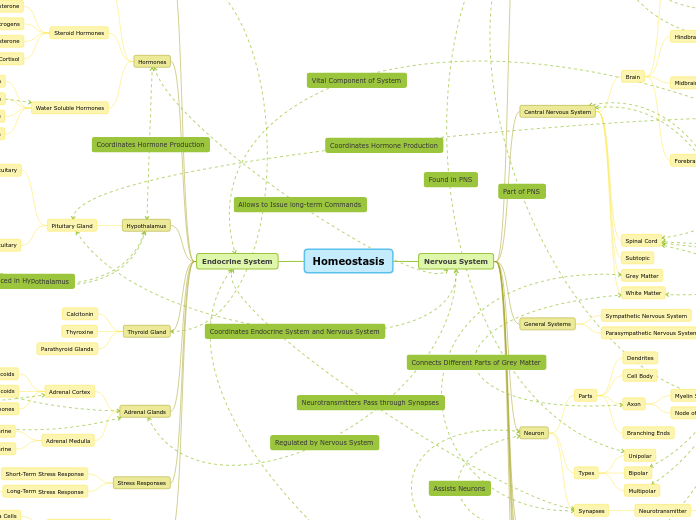
Homeostasis
Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Afferent System
Efferent System
Somatic Nervous System
Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Central Nervous System
Brain
Protective Mechanisms
Meninges
Astrocytes
Blood-Brain Barrier
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Hindbrain
Cerebellum
Subtopic
Medulla Oblongta
Pons
Midbrain
Forebrain
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Cerebrum
Cerebral Cortex
Occipital Lobes
Temporal Lobes
Parietal Lobes
Frontal Lobes
Corpus Callosum
Spinal Cord
Subtopic
Grey Matter
White Matter
General Systems
Sympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Neuron
Parts
Dendrites
Cell Body
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Schwann Cell
Node of Ranvier
Branching Ends
Types
Unipolar
Bipolar
Multipolar
Synapses
Neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine
Glial Cells
Nerves
Ganglia
Reflex Arc
Nerve Impulse
Membrane Potential
Resting Membrane Potential
Action Potential
Threshold Potential
Refractory Period
Saltatory Conduction
Endocrine System
Endocrine Glands
Hormones
Tropic Hormones
Steroid Hormones
Testosterone
Estrogens or Oestrogens
Aldosterone
Cortisol
Water Soluble Hormones
Epinephrine or Adrenalin
Human Growth Hormone
Thyroxine
Insulin
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Posterior Pituitary
Antidiuretic Hormone
Oxytocin
Anterior Pituitary
Luteinizing Hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Hyman Growth Hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
Thyroid Gland
Calcitonin
Thyroxine
Parathyroid Glands
Adrenal Glands
Adrenal Cortex
Glucocorticoids
Mineralocorticoids
Sex Hormones
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Stress Responses
Short-Term Stress Response
Long-Term Stress Response
Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
Cortisol
Pancreas
Islets of Langerhans
Beta Cells
Insulin
Alpha Cells
Glucagon
Diabetes Mellitus