Listening and L2
Language comprehension
Individual linguistic units
Phonemes, words, gramatical structures, background knowledge.
Linguistic skills
Cognitive skills
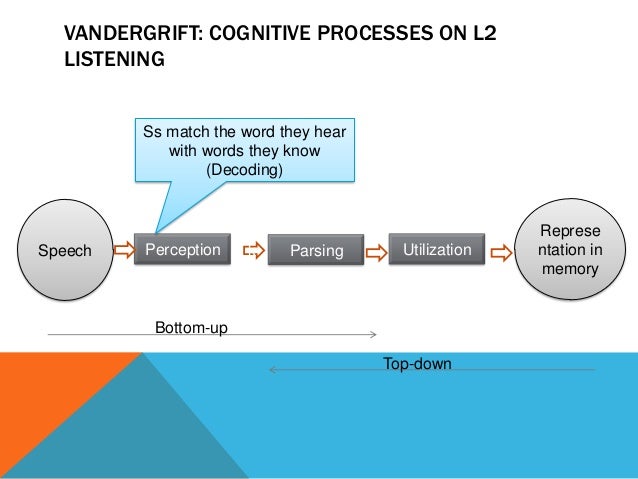
First stage
Sounds go to the echoic memory.
Second stage
Sounds are processed by the short-term memory, meaning is extracted.
Third stage
Listener is able to construct meaning, information can be transferred to the long-term memory.
Schema theory
Bottom-up processing
Movement of data from page to brain.
Top-down processing.
Brain tries to find existing knowledge and assimilate new data.
Rixon
meaning in context, connected speech, language rythm.
Ur
Problems of sounds
pronunciation, rhythm, intonation and stress
Inability to skim information
redundancy, noise, and the inability to guess
Lacking exposure
Different accents, colloquial vocabulary.
Inability to link words in context

unskillful in using strategies to summarize heard information at the macro-level and micro-level.
Topic principal

Assisting listening skills

Focus on meaning and finding new important content in the L2.
Focus on specific goals.
Using meaning-oriented tasks.
My background
I need to provide more comprehensible imput, teach strategies to improve the listening skills.