LISTENING Ilse Naomi Jaime Tanamachi, November 7th, 2021 Teaching Language as Communication
The listening process
First stage
The sounds go into the “echoic” memory and are organized into meaningful units
Second stage
The processing of the information by the short-term memory
Final stage
The listener is able to construct a meaning from the utterance.
Subtopic
The schema theory
Knowledge is represented and that representation facilitates the use of the knowledge.
Bottom-up processing.
Triggers certain past experiences or perceptions about the topic
Top-down processing
Find an existing knowledge structure to facilitate the assimilation of new information.

Difficulties in listening to English in EFL classroom
Listening in EFL classroom
Understand the words
Understand the context
Teacher's responsibilities
Understand their learners’ needs
Visualize the objectives and means of the stages
Set meaningful, focused and graded listening tasks
Encourage more participations in activities and tasks in classroom
Starting out by listening to English (instead of speaking it) helps your brain retain basic knowledge about what sounds best in English.
Self-access outside the Classroom
Use of real material
Tapes/videos/DVD as self-access study materials.

Fairy tales, like cartoons for learning English, are ideal for my young students. The language is direct and the stories are easy to follow. There is also a lot of repetition, which can help you remember the plot and memorize the new vocabulary.
Selecting right topics
Interest of learners
Right level
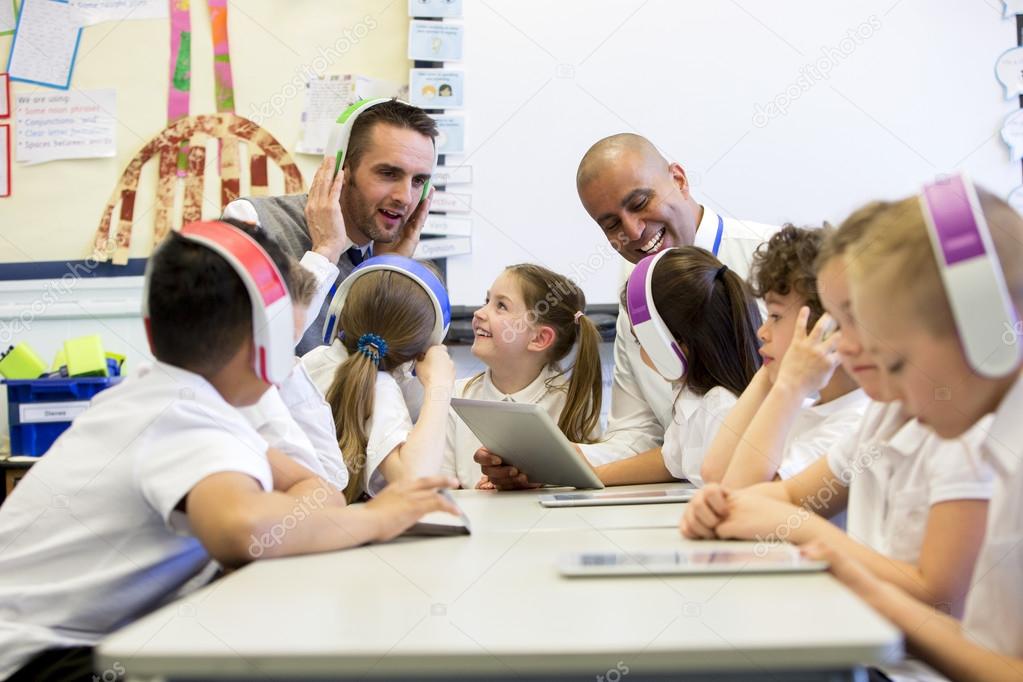

If students enjoy their listening practice, they will be inclined to continue practicing and improving listening skills.
Develop students listening skills
Focusing on meaning
Mobilize both their linguistic and non-linguistic abilities to understand what is heard
Working on comprehension activities
Learners have opportunities for assessing and revising what they have achieved
Attention to accuracy and an analysis of form
Learners gain confidence in listening for meaning