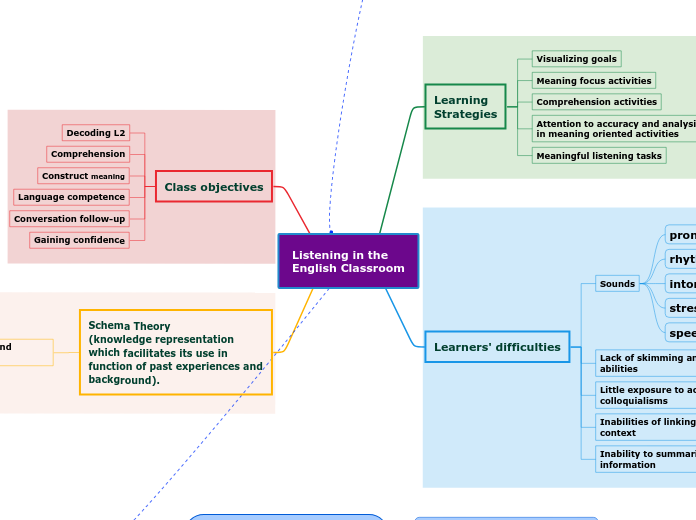
Listening in the
English Classroom
Learning
Strategies
Visualizing goals
Meaning focus activities
Comprehension activities
Attention to accuracy and analysis in meaning oriented activities
Meaningful listening tasks
Learners' difficulties
Sounds
pronounciation
rhythm
intonation
stress
speed
Lack of skimming and guessing abilities
Little exposure to accents and colloquialisms
Inabilities of linking words to context
Inability to summarize heard information
Class objectives
Decoding L2
Comprehension
Construct meaning
Language competence
Conversation follow-up
Gaining confidence
Schema Theory
(knowledge representation which facilitates its use in function of past experiences and background).
Simultaneous, symbiotic and complementary processes
Bottom-up processing
(triggers past experiences and perceptions)
Top-down processing
(take up existing knowledge structure to facilitate the assimilation of new data)
Listening process
Sounds go to the echoic memory to be organized into units with previous knowledge.
Information is processed by short-term memory, compared to stored info. and its meaning extracted.
Meaning construction, that might be sent to the long-term memory.
Personal teaching experience
To do
Improve lesson planning
Dedicate more time to listening comprehension
Better choosing of listening activities
Expose students to a diversity of accents
Done
Include listening tasks focused on meaning.
Assess listening in quizzes and exams