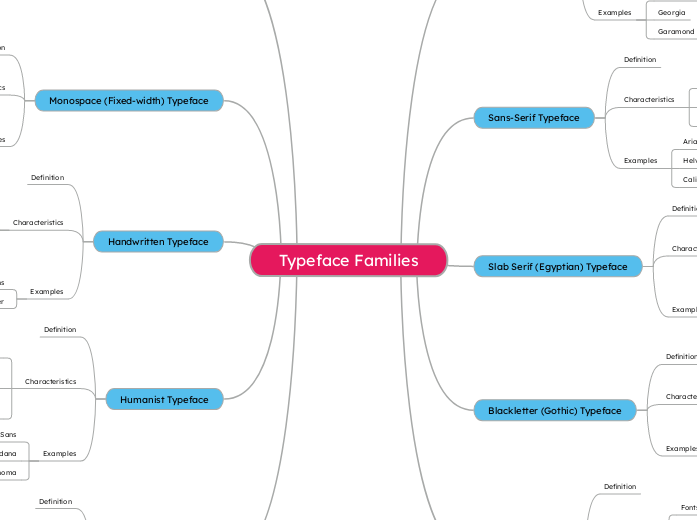
Typeface Families
Serif Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Small lines or strokes attached to the ends of letters
Commonly used in books and newspapers
Classic and readable
Examples
Times New Roman
Georgia
Garamond
Sans-Serif Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Fonts without serifs
Clean and modern look
Common in digital and web design
Examples
Arial
Helvetica
Calibri
Slab Serif (Egyptian) Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Thick
block-like serifs
Bold and attention-grabbing
Often used in posters or headlines
Examples
Rockwell
Courier
Museo Slab
Blackletter (Gothic) Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Old
medieval-style fonts with dramatic strokes
Traditional or historic look
Used in certificates or logos
Examples
Old English Text
Fraktur
Script Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Fonts that mimic handwriting or calligraphy
Elegant or casual
depending on style
Used in invitations
logos
or artistic projects
Examples
Brush Script
Pacifico
Edwardian Script
Display (Decorative / Novelty) Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Highly stylized fonts for titles and headings
Not suitable for body text
Used to create a unique vibe or visual impact
Examples
Jokerman
Lobster
Impact
Monospace (Fixed-width) Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Each letter takes up the same amount of space
Great for coding and tabular data
Clear and aligned text
Examples
Courier New
Consolas
Handwritten Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Imitates natural handwriting
Casual and personal feel
Used in comics
notes
or casual branding
Examples
Comic Sans
Indie Flower
Humanist Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Inspired by handwriting and classic proportions
Easy to read
with warm
organic shapes
Found in both serif and sans-serif versions
Examples
Gill Sans
Verdana
Tahoma
Geometric Typeface
Definition
Characteristics
Based on geometric shapes like circles and squares
Modern and structured look
Often used in logos and tech design
Examples
Futura
Avenir
Gotham