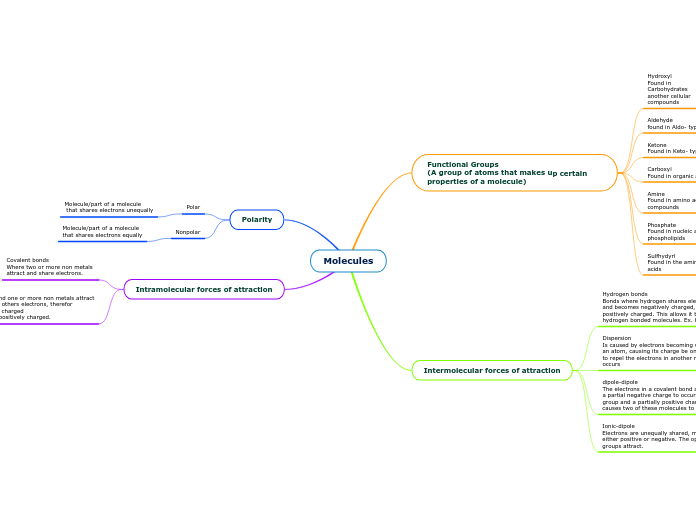
Molecules
Functional Groups
(A group of atoms that makes up certain properties of a molecule)
Hydroxyl
Found in Carbohydrates another cellular compounds
Aldehyde
found in Aldo- type sugars
Ketone
Found in Keto- type sugars
Carboxyl
Found in organic acids such as amino acids and fatty acids
Amine
Found in amino acids, proteins and other N- containing compounds
Phosphate
Found in nucleic acids (DNA, RNA), ATP, ADP, and phospholipids
Sulfhydyrl
Found in the amino acid cystine, therefore also in most amino acids
Intermolecular forces of attraction
Hydrogen bonds
Bonds where hydrogen shares electrons with another atom and becomes negatively charged, and the other atom becomes positively charged. This allows it to connect with other hydrogen bonded molecules. Ex. H2O
Dispersion
Is caused by electrons becoming unevenly distributed around an atom, causing its charge be on one side of it. This causes it to repel the electrons in another molecule, therefor attraction occurs
dipole-dipole
The electrons in a covalent bond are shared unequally causing a partial negative charge to occur at one end of the functional group and a partially positive charge on the other end. This causes two of these molecules to attract.
Ionic-dipole
Electrons are unequally shared, making the functional group either positive or negative. The oppositely charges functional groups attract.
Polarity
Polar
Molecule/part of a molecule
that shares electrons unequally
Nonpolar
Molecule/part of a molecule
that shares electrons equally
Intramolecular forces of attraction
Covalent bonds
Where two or more non metals
attract and share electrons.
Ionic bonds
Where a metal and one or more non metals attract
by stealing each others electrons, therefor
one is negatively charged
and the other is positively charged.