Muscles
3 Types
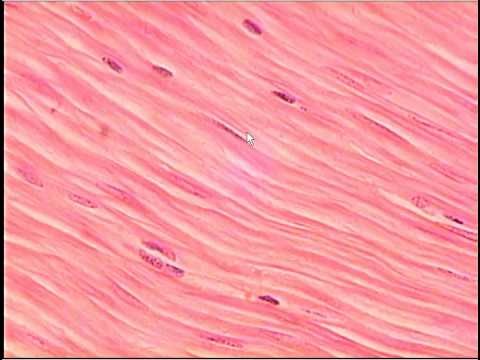
Smooth Muscle
Found in the wall of organs
Control breathing, movements
of digestive system, keeps organs
functioning involuntarily
Not striated

Cardiac Muscle
Only found in the heart
Control heart beat
Striated

Skeletal Muscle
Found generally
around bones
4 Types
Prime Movers
Antagonists
Synergists
Fixators
Stabilize joints against dislocation
Help prime by lending extra power
Work in reverse, abduction
Agonists, adduction
Sliding Filament
Model
Shows how skeletal
muscles work
Striated
Twitches
Latent Period
Stimulent has
arrived, no force
Period Of Contraction
Binding and pulling
of muscles
Tetanus
All little twitches blend
together until they feel like
one large contraction
Relaxation Period
Calcium gets pumped into
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Motor Units
Group of muscle fibers
that get all their signals from
the same single motor neuron
Small muscle units= fine
motor skills
Contains actin and
myosin, proteins
Two types of
contractions
Isotonic
Change in length
Isometric
No change in length