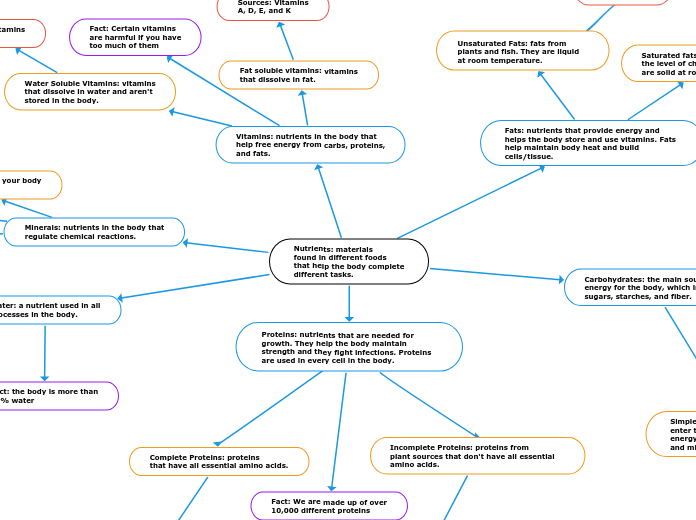
Nutrients: materials
found in different foods
that help the body complete
different tasks.
Proteins: nutrients that are needed for
growth. They help the body maintain
strength and they fight infections. Proteins are used in every cell in the body.
Complete Proteins: proteins
that have all essential amino acids.
Sources: Meat, fish,
poultry, milk, yogurt,
and eggs
Incomplete Proteins: proteins from
plant sources that don't have all essential amino acids.
Sources: Grains,
legumes, nuts, and seeds
Fact: We are made up of over
10,000 different proteins
Carbohydrates: the main source of
energy for the body, which include
sugars, starches, and fiber.
Simple carbohydrates: Sugars that
enter the bloodstream and are quick
energy. They are few in vitamins and minerals
Sources: Naturally in fruits, honey and milk.
It is added to foods like cake, candy, ketchup, and soda during processing as sugar.
Complex Carbohydrates: the source
of most calories in your diet. Starches
and fiber are considered complex carbs.
Sources: Bread, pasta,
potatoes, and beans
Fiber: helps prevent intestinal problems,
reduces the risk of colon cancer, and can
reduce blood cholesterol.
Sources: grains, breads, cereal,
seeds, dried beans, fruits, and veggies.
Fact: The body breaks down
carbs into glucose
Fats: nutrients that provide energy and
helps the body store and use vitamins. Fats
help maintain body heat and build cells/tissue.
Saturated fats: these contribute to
the level of cholesterol in blood and
are solid at room temperature.
Sources: Dairy products,
meat, and poultry.
Trans-fatty acids: formed when vegetable oils are processed into solid fat.
Sources: shortening, margarine, crackers, cookies, donuts, and snack foods
Fact: Fats are made of fatty acids,
which the body can't produce itself.
Vitamins: nutrients in the body that
help free energy from carbs, proteins,
and fats.
Fat soluble vitamins: vitamins
that dissolve in fat.
Sources: Vitamins
A, D, E, and K
Water Soluble Vitamins: vitamins
that dissolve in water and aren't
stored in the body.
Sources: Vitamins
C and B
Fact: Certain vitamins
are harmful if you have
too much of them
Minerals: nutrients in the body that
regulate chemical reactions.
Macro molecules: minerals that your body
needs more than 100 mg of
Sources: Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus,
Potassium, Sodium, and Sulfur
Trace molecules: Minerals
that your body needs a small
amount of
Sources: Copper, Iodine,
Iron, Manganese, and Zinc
Fact: Minerals are used to keep bones,
muscles, heart, and the brain working
Water: a nutrient used in all
processes in the body.
Source: Just drinking water!
Fact: the body is more than
60% water