INGLÉS 5TO AÑO
Future Be Going To: Affirmative And Negative Form
Es un tiempo verbal que tiene dos usos:
-Planes e intenciones.
-Predicciones basadas en evidencias.
(Habla de un futuro cercano)
I am going to see you tomorrow.
He is going to visit her next week.
They are going to eat out tonight.
I'm not going to see you tomorrow.
He isn't going to visit her next week.
They aren't going to eat out tonight.
Affirmative: Subject+am/is/are+going to+verb+complement
Negative: Subject+am not/isn't/aren't+going to+verb+complement
Future Be Going To: Interrogative form and short answers
Interrogative: Is/Are + subject + going to + verb + complement.
Are you going to see me tomorrow? Yes, I am. / No,I'm not.
Is he going to visit her next week? Yes, he is. / No, he isn't.
Time expressions
Tomorrow
Morning / Afternoon / Evening
This mornening / Afternoon / Evening
Tonight
The next day / week / month / year
The following day / week / month / year
in a hour
Later
Future simple Will: Affirmative, negative, interrogative and short amswers.
El futuro simple es un verbo modal (porque se conjuga con todos los pronombres) que se utiliza para describir acciones que se van a desarrollar en un futuro, sin necesidad de especificar cuándo. (Indica un futuro lejano).
Affirmative:I will work.
You/they/we will work.
He/she will work.
Negative: I won't work.
You/they/we won't work.
He/she won't work.
Interrogative: Will you work? Yes, I will/No, I won't.
Will you/they/we work? Yes, you/they/we wil/ No, you/they/we won't.
Will He/she work? Yes, he/she will/No, He/she won't.
Present Perfect: Affirmative, negative, interrogative form and short answers.
Una acción o situación iniciada en el pasado y que continúa en el presente.
-I have/haven't lived in Bristol since 1984 (= todavía vivo allí.)
-Have you lived un Bristol since 1984?
Una acción empezada en el pasado que aún continua.
-She has/hasn't studied English for ten yers.
-Has she estudied for ten years?
A: subject + have / has + past participle + complement.
N: subject + haven't / hasn't + past participle + complement.
I: Have/Has + subject + past participle + complement + ?.
Pronouns/Pronombres:
-Have: I / you / we / they.
-Has: He / she / it.
Para hablar de experiencias en nuestras vidas sin decir cuando ocurrieron.
-I have/haven't been in Canada.
-Have you been in Canada?
Present Perfect: For - Since - Never - Ever - Already - Yet
Los adverbios "ever" y "never" se refieren a un tiempo no identificado, anterior al presente
-Have you ever visited Berlin?
"Never" significa nunca antes de ahora.
-I have never visited Berlin.
"Already" se refiere a una acción que ha ocurrido en un tiempo anterior al presente pero no especificado. -I've already drunk three coffees this morning.
-(Tambien:) Have you already written to John?
"Yet" se utiliza en oraciones negativas e interrogativas, con el significado de (no) en el periodo temporal entre el pasado y el ahora, (no) hasta el momento presente, incluido éste. Suele colocarse al final de la frase.
-Have you met Judy yet?
-I haven't visited the Tate Gallery yet.
"Since" se usa para hablar desde un punto de tiempo.
-She has lives here since 1998.
"For" se usa para hablar de un periodo de tiempo.
-She has lives here for three years.
Past participle: Been / Gone
Se usa el presente perfecto de "have/has been" para hablar de algo que fue a un lugar y ya volvió.
-Alan have been to China. He really liked it.
Se usa el presente perfecto de "have/has been" para hablar de algo que fue a algun lugar pero que sigue ahi.
-Maria has gone out, She'll back soon.
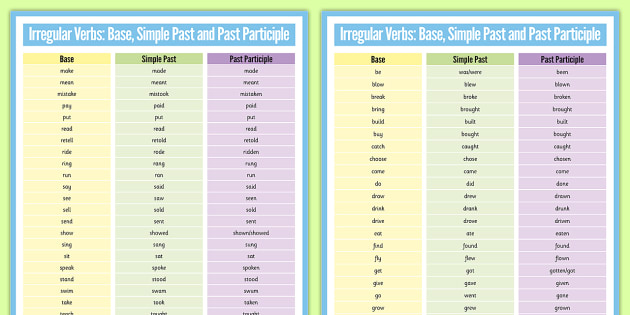
Base form - Past simple - Past participle Verbs