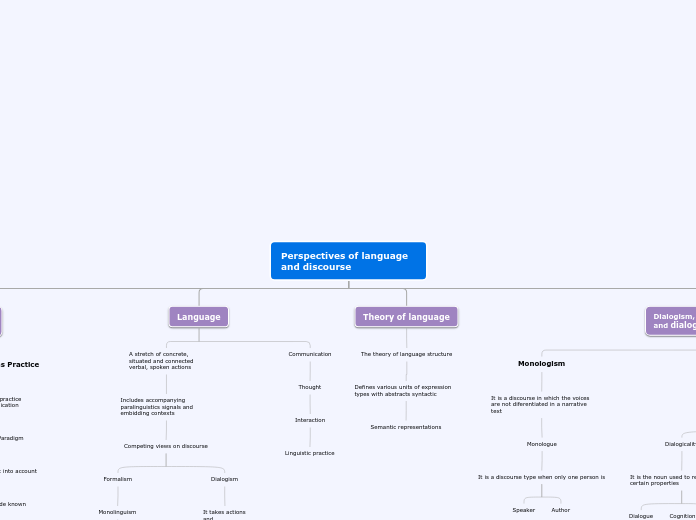
Perspectives of language and discourse
Language as system vs. Language as practice
Language as System
System or Structure
Formalist Framework
Linguistic expressions can be treated in abract
Voucabulary
'Sentence', 'noun', 'grammatical subject', etc.
Semantic representations
Units of structure
Language as Practice
Discourse, practice or communication
Formalist Paradigm
To take context into account
What is made known
What it said
Vocabulary
'Utterance', 'interpretation', 'message', 'context', etc.
It is seen as secondary 'language use'
Discourse Aspects
Language is seen as representational
Language
A stretch of concrete, situated and connected verbal, spoken actions
Includes accompanying paralinguistics signals and embidding contexts
Competing views on discourse
Formalism
Monolinguism
The dominant paradigm in the language
It assumes individuals and societies to be analytical primes
It is the accepted mainstream epistemology of major traditions of the language science
Dialogism
It takes actions and interactions
Theory of human actions and activitie in cognitive and interactive contexts
Communication
Thought
Interaction
Linguistic practice
Theory of language
The theory of language structure
Defines various units of expression types with abstracts syntactic
Semantic representations
Dialogism, dialogicality and dialogue
Monologism
It is a discourse in which the voices are not diferentiated in a narrative text
Monologue
It is a discourse type when only one person is
Speaker
Author
Dialogism
Expressing ideas or feelings in the form of dialogue
Dialogicality
It is the noun used to refer to certain properties
Dialogue
Cognition and communication
Dialogue
About any dyadic or polyadic interaction between individuals
Mutually co-present to each other
Interact through language