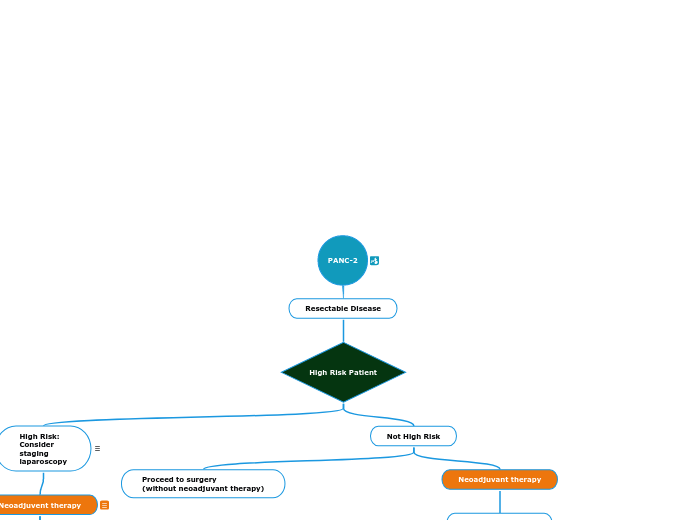
PANC-2
Resectable Disease
High Risk Patient
High Risk:
Consider
staging
laparoscopy
Neoadjuvent therapy
PANC-F
PANC-G
Not High Risk
Proceed to surgery
(without neoadjuvant therapy)
Neoadjuvant therapy
EUS guided biopsy
Pancreatic CT/MRI
Chest/Pelvic CT
Surgery
Successful
Resection?
PANC-5
PANC-4
CA 19-9
Stent
PANC-B