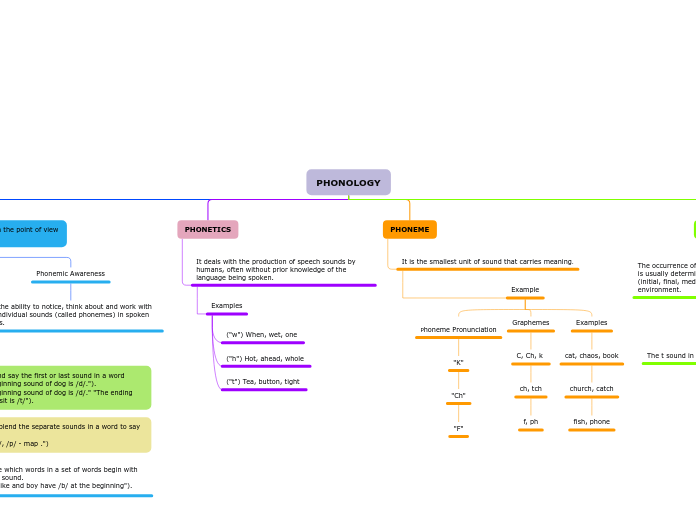
PHONOLOGY
It studies the phonic elements from the point of view of their function.
Phonological awareness
Composed of a group of skills that include being able to identify rhyming words, count the number of syllables in a noun, recognize alliteration, segment a sentence into words, and identify the syllables in a word.
Phonemic Awareness
It is the ability to notice, think about and work with the individual sounds (called phonemes) in spoken words.
PHONETICS
It deals with the production of speech sounds by humans, often without prior knowledge of the language being spoken.
Examples
("w") When, wet, one
("h") Hot, ahead, whole
("t") Tea, button, tight
PHONEME
It is the smallest unit of sound that carries meaning.
Example
Phoneme Pronunciation
"K"
"Ch"
"F"
Graphemes
C, Ch, k
ch, tch
f, ph
Examples
cat, chaos, book
church, catch
fish, phone
ALLOPHONE
The occurrence of one allophone in place of another is usually determined by its position in the word (initial, final, medial.) or by its phonetic environment.
Example
The t sound in the words "hit", "tip" and "little".
( file ) `FaIt
( fool ) `Fut
( feel ) `fit