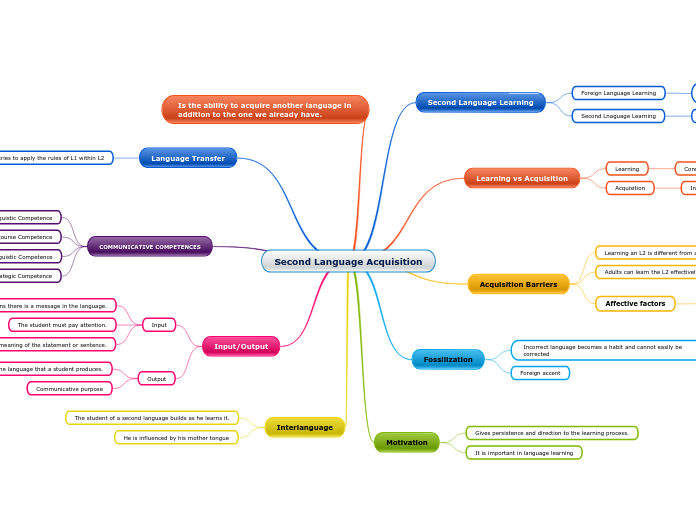
Second Language Acquisition
Second Language Learning
Foreign Language Learning
learning a language that is not spoken in the native community
Second Lnaguage Learning
Learning a language that is spoken outside the community
Learning vs Acquisition
Learning
Conscious process
Formal knowledge of rules
Acquisition
Inconscious process
Acquired in our environment
Acquisition Barriers
Learning an L2 is different from an L1
With this language they can communicate
Adults can learn the L2 effectively
do not sound like natives
Affective factors
Negative experiences that affect learning
Lack of empaty
Dull texbooks and classrooms
Fossilization
Incorrect language becomes a habit and cannot easily be corrected
Foreign accent
Motivation
Gives persistence and direction to the learning process.
It is important in language learning
Is the ability to acquire another language in addition to the one we already have.
Language Transfer
The learner tries to apply the rules of L1 within L2
Positive Transfer
Transfer of a feature from L1 that is similar from L2
Negative Transfer
Transfer of a characteristic from L1 that is different from L2
COMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCESundefined
Linguistic Competence
Discourse Competence
Socio-Linguistic Competence
Strategic Competence
Input/Output
Input
It means there is a message in the language.
The student must pay attention.
Understand the meaning of the statement or sentence.
Output
It is the language that a student produces.
Communicative purpose
Interlanguage
The student of a second language builds as he learns it.
He is influenced by his mother tongue