Seizure
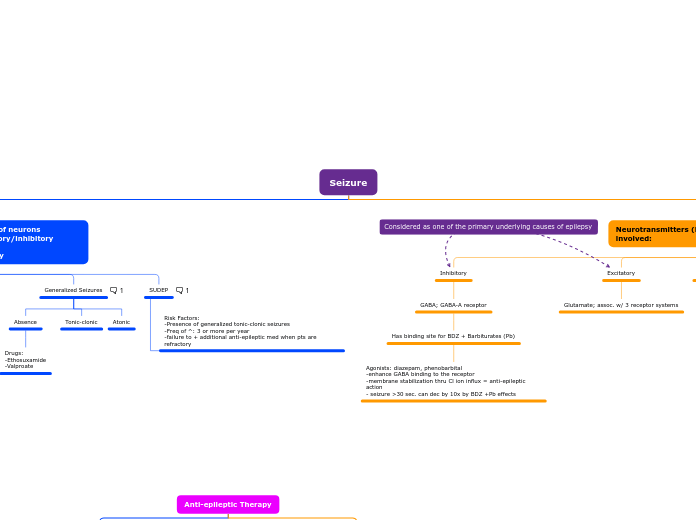
-Paroxysmal discharge of neurons
-imbalance b/w excitatory/inhibitory neurotransmission
-neurons fire abnormally
Myoclonic seizure causes:
Juvenile Myoclonic epilepsy (JME)
Lennox Gastaut syndrome (LGS)
Rett syndrome
Progressive Myoclonic epilepsy
Dravet syndrome
Fenfluramine
Partial Seizures
Simple
Complex
Generalized Seizures
Absence
Drugs:
-Ethosuxamide
-Valproate
Tonic-clonic
Atonic
SUDEP
Risk Factors:
-Presence of generalized tonic-clonic seizures
-Freq of ^: 3 or more per year
-failure to + additional anti-epileptic med when pts are refractory
Neurotransmitters (NT) and ion channels involved:
Inhibitory
GABA; GABA-A receptor
Has binding site for BDZ + Barbiturates (Pb)
Agonists: diazepam, phenobarbital
-enhance GABA binding to the receptor
-membrane stabilization thru Cl ion influx = anti-epileptic action
- seizure >30 sec. can dec by 10x by BDZ +Pb effects
Excitatory
Glutamate; assoc. w/ 3 receptor systems
Ion Channels
Axon potential at presynaptic nerve terminal (Ca2 channel) releases NT
GABA-B receptors activated by axon potential decrease Ca2+ influx and inhibit NT release
Pathophys:
-NT's move across the synaptic cleft
Anti-epileptic Therapy
Non-pharm
Nerve stimulators- Vegal Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
-Changes CSF Cpss of inhibitory and stimulatory NTs
-Very safe: voice change, hoarse, coughing, nausea
Surgery: refractory focal epilepsy
Ketogenic diet (high fat, low carb and protein
Modified Atkins diet used in peds.
Pharm: Start tx, most benefit w/ 1st or 2nd agents
-Many guidelines
-Focus on dosing and serum concentration ranges to adjust therapy
Phenytoin: total and unbound
Valproic acid (VPA): widest range (!50mcg/mL)
Carbamazepine (CBZ): toxicity can be fatal
Therapy Map
Generalized/Multifocal onset
Tonic
Atonic
Atypical Absence
GTC
Spasms?
No
Valproate
Rufinamide
Clobazam
Lamotrigine
Yes
Vigabatrin
ACTH (ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE)
Generalized/bihemispheric seizures
Absence
Ethosuxamide
Myoclonic
Primary GTC
Absence
Focal seizures
Simple partial
Complex partial
Secondary GTC
Narrow Spectrum:
-Lacosamide
-Pregabalin
-Gabapentin
-Carbamazepine
-Oxcarbazepine
-Eslicarbazepine
-Phenytoin
-Vigabatrin
-Ezogabine
-Tiagabine
When need to step up therapy/add another agent or just not sure of the specific seizure:
-Levetiracetam
-Lamotrigine
-Topiramate
-Zonisamide
-Valproate
-Clobazam
-Rufinamide
-Felbamate
-Perampanel
-Phenobarbital
-Primidone
-Clonazepam
Pharmacokinetics (PK)
Linear PK: dose/conc. proportional r/s
Phenobarbital
Valproic acid (VPA dose <2.5)
Mephenytoin
Felbamate
Levetiracetam
Oxcarbazepine
Lamotrigine
Zonisamide
Tiagabine
Topiramate
Non-linear PK
Type A
Phenytoin
Ethotoin
Type B
VPA (doses >2.5gm/day)
Ethosuximide (dose >1.5gm)
Gabapentin
Pregabalin (GI absorption^)
Carbamazepine (CBZ, auto-induction)