Sigit_Covey_Vanya_yessica
Electromagnetic Waves
Effects of Electromagnetic Waves
Heating
When water absorbs micorwaves, they are warmed up
The burning of coal gives out infrared radiation as heat to the surrounding
Ionising
Ultra-violet rays are highly energetic
Able to ionise atoms which can be harmful to living tissues
Under excessive expore to UV rays can cause sunburn and skin cancer
Damage to living cells and tissues
Gamma ray is ionising radiation
It is used to treat tumour cells. However it could damage the surrounding cells and tissues which absorb the rays
Characteristics of Electromagnetic Waves
1) Can pass through vaccum
2) They are transverse waves
3) All show waves properties like refraction and reflection
4) They obey the wave equation v=fλ
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
Types of Electromagnetic Waves
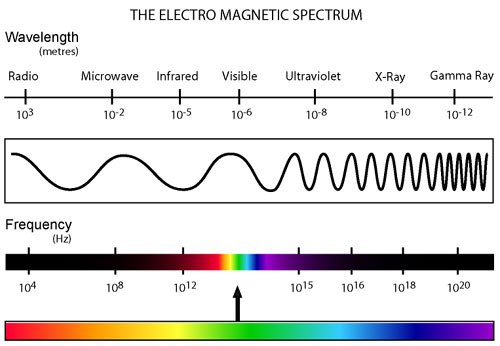
Uses of Radio Waves
Transmit television and radio programmes.
Uses of Microwaves
1. Transmit signals such as mobile phone calls.
2. Heat up food particles.
Uses of Infrared
1. Optical fibre.
2. Burglar alarms.
3. Remote controls for television sets and DVD player.
Uses of Visible Light
1. Enabling us to see.
Uses of Ultraviolet Ray
1. Detecting forged bank notes by fluorescence.
2. Fluorescent lights.
Uses of X-ray
1. Look into a person's body to discover their illnesses or injuries.
2. Check the contains of luggages in immigration offices and airports.
Uses of Gamma Rays
1. Kill cancer cells.
2. kill harmful bacteria in food.
3. Sterilise surgical instruments.
Sounds
Propagation of Sound
Compression
When the a vibration in the air causes
the air to be pressed together
This causes the air particles
to be pressed together.
Rarefaction
when a preceedding
compression
left a decompression
wave in it's
wake and causes a
rarefaction to occur.
This causes the air particles
to be pulled apart.
Graphical Representation of waves
Displacement-Position Graph
Subtopic
Displacement-Time Graph
Main topic
Wave Terms
Names of used in a wave graph
Wave front
The line that joins all
the wave or all identical
points on a wave.
Crest
Positive amplitude;
highest point in the
graph/wave.
Trough
Negative amplitude;
lowest point in the
graph/wave.
Amplitude
a; maximum dissplacement
from rest (centre of the graph)
determines how high the crest is
and how low the trough is.
Wavelength
λ; distance between two
successive crest or trough
points on successive waves.
Frequency
f; number of point passing
through a point per second.
Unit of frequency hertz (Hz).
Equivalent to the number of
complete waves generated
per second.
Period
T; time taken to generate one
complete wave.
Also the time taken for any point
to move 1 wavelength away.
T=f^-1
Speed
V; distance moved by one
wave in one second
V = λ/T
V = fλ
Effects on Sound waves
Longitudinal Waves
With the compression and
rarefaction occuring
simultaneously,
it creates a sound wave.
The sound waves travel parallel
to the direction of the sound
and causes the sound to be
carried away.