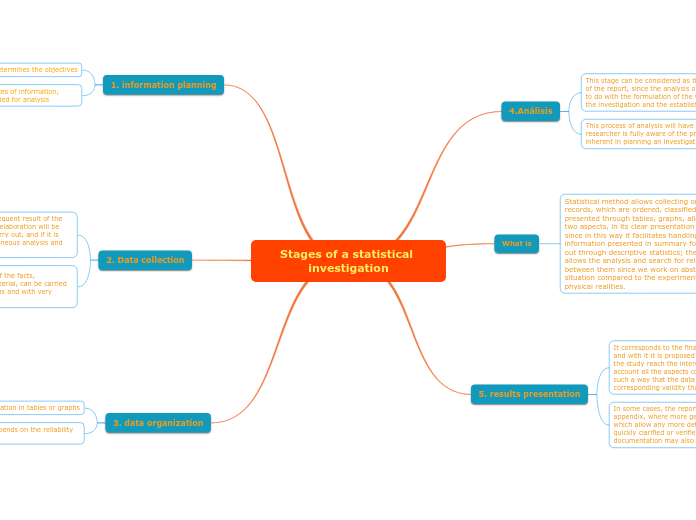
Stages of a statistical investigation
4.Análisis
This stage can be considered as the most important of the report, since the analysis of the data will have to do with the formulation of the very objective of the investigation and the established hypotheses.
This process of analysis will have less difficulty if the researcher is fully aware of the problems that are inherent in planning an investigation.undefined
What is
Statistical method allows collecting or observing through records, which are ordered, classified, quantified and presented through tables, graphs, allowing data purification in two aspects, in its clear presentation and in its simplification, since in this way it facilitates handling large amounts of information presented in summary form, a task that we carry out through descriptive statistics; then statistical inference allows the analysis and search for relationships that may exist between them since we work on abstractions, a very different situation compared to the experimental method that rests on physical realities.
5. results presentation
It corresponds to the final phase of the investigation, and with it it is proposed to make the total result of the study reach the interested persons, taking into account all the aspects considered in the process, in such a way that the data is understandable, with the corresponding validity that the conclusions deserve.undefined
In some cases, the report has a final part, called an appendix, where more general tables are included, which allow any more detailed information to be quickly clarified or verified. Supplementary documentation may also be included in the report.undefined
1. information planning
Bases and determines the objectivesundefined
Identifies and evaluates sources of information, population and elements studied for analysis
2. Data collection
On this task depends all the subsequent result of the statistics. If it is poorly done, the elaboration will be incorrect or even impossible to carry out, and if it is carried out, it will give rise to erroneous analysis and false interpretations.
3. data organization
organization and classification in tables or graphs
The validity of the results depends on the reliability of the data used.undefined