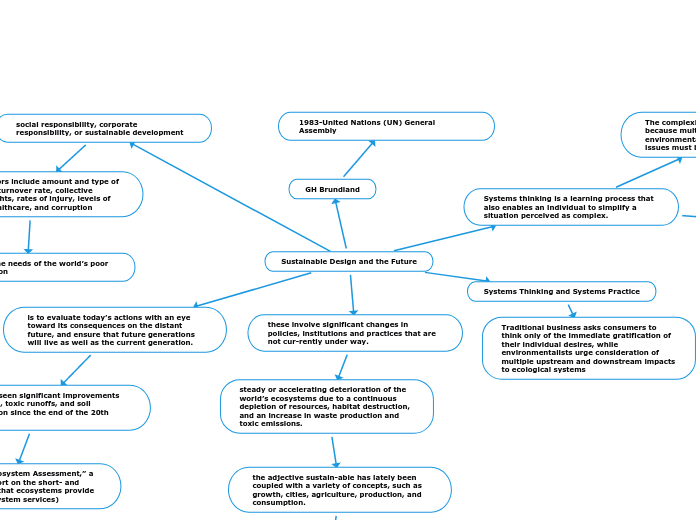
Sustainable Design and the Future
GH Brundland
1983-United Nations (UN) General Assembly
is to evaluate today’s actions with an eye toward its consequences on the distant future, and ensure that future generations will live as well as the current generation.
which have seen significant improvements in water use, toxic runoffs, and soil contamination since the end of the 20th century.
The “Millennium Ecosystem Assessment,” a comprehensive report on the short- and long-term benefits that ecosystems provide for humanity (ecosystem services)
these involve significant changes in policies, institutions and practices that are not cur-rently under way.
steady or accelerating deterioration of the world’s ecosystems due to a continuous depletion of resources, habitat destruction, and an increase in waste production and toxic emissions.
the adjective sustain-able has lately been coupled with a variety of concepts, such as growth, cities, agriculture, production, and consumption.
various economic players (investors, consumers, and industries) would constitute a type of sustainable development that has been called “ecological modernization.”
Systems thinking is a learning process that also enables an individual to simplify a situation perceived as complex.
The complexity in green business arises because multiple competing economic, environmental, technological, and social issues must be considered
•is an organized assembly of interconnected components;•consists of a number of subsystems, the behavior of which is affected by being in the system, and which change the behavior of the system by leaving it;•does something;•is identified by someone because he is interested in it
Systems Thinking and Systems Practice
Traditional business asks consumers to think only of the immediate gratification of their individual desires, while environmentalists urge consideration of multiple upstream and downstream impacts to ecological systems
social responsibility, corporate responsibility, or sustainable development
Social indicators include amount and type of employment, turnover rate, collective bargaining rights, rates of injury, levels of education, healthcare, and corruption
Report citing the needs of the world’s poor in their definition