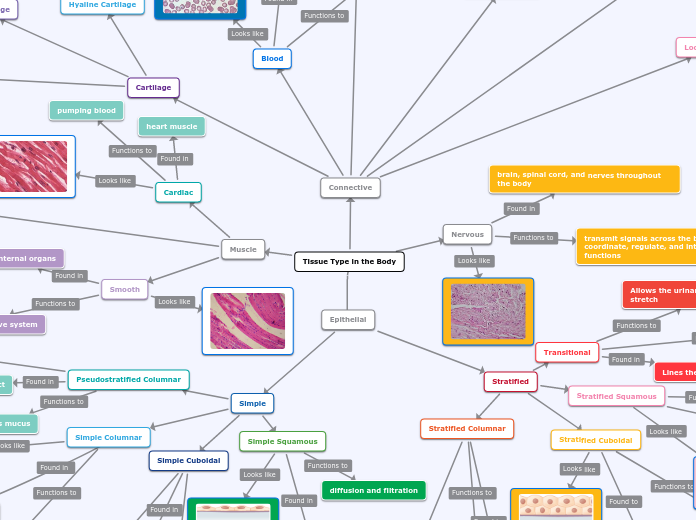
Tissue Type in the Body
Epithelial
Simple
Simple Squamous

air sacs of lungs, heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels
diffusion and filtration
Simple Cuboidal

kidney tubules
Secretes and absorbs
Simple Columnar

digestive tract bladder
absorbs and secretes mucus and enzymes
Pseudostratified Columnar

trachea and upper respiratory tract
secretes mucus
Stratified
Stratified Columnar

male urethra and ducts of some glands
secretes and protects
Stratified Cuboidal

absorption, secretion, and excretion
Sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands
Stratified Squamous

Lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Protects against abrasion
Transitional

Lines the bladder, urethra and ureters
Allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
Connective
Loose or Areolar

surrounds blood vessels and supports internal organs
binds underlying organs to skin and to each other and forms delicate thin membranes throughout the body
Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
external ear and larynx
maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility

Fibrocartilage

between vertebrae
tough, shocking absorbing
Hyaline Cartilage

covers end of joints, nose, respiratory passages
padding
Dense Fibrous

in dermis of skin, tendons, and ligaments
support
Bone(Osseous)

all over the body
gives strength and flexibility to the tissue
Adipose (fat)

beneath the skin and around internal organs
a protective cushion, insulation, and stores energy
Blood

every blood vessel
transports oxygen to body tissues
Muscle
Cardiac

pumping blood
heart muscle
Skeletal
attached to bones

pull bones and skin
Smooth
pushes food through digestive system
walls of hollow internal organs

Nervous

transmit signals across the body and coordinate, regulate, and integrate bodily functions
brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body