Tissue Types
Epithelial
Simple squamous
diffusion n filtration
air sacs in lungs

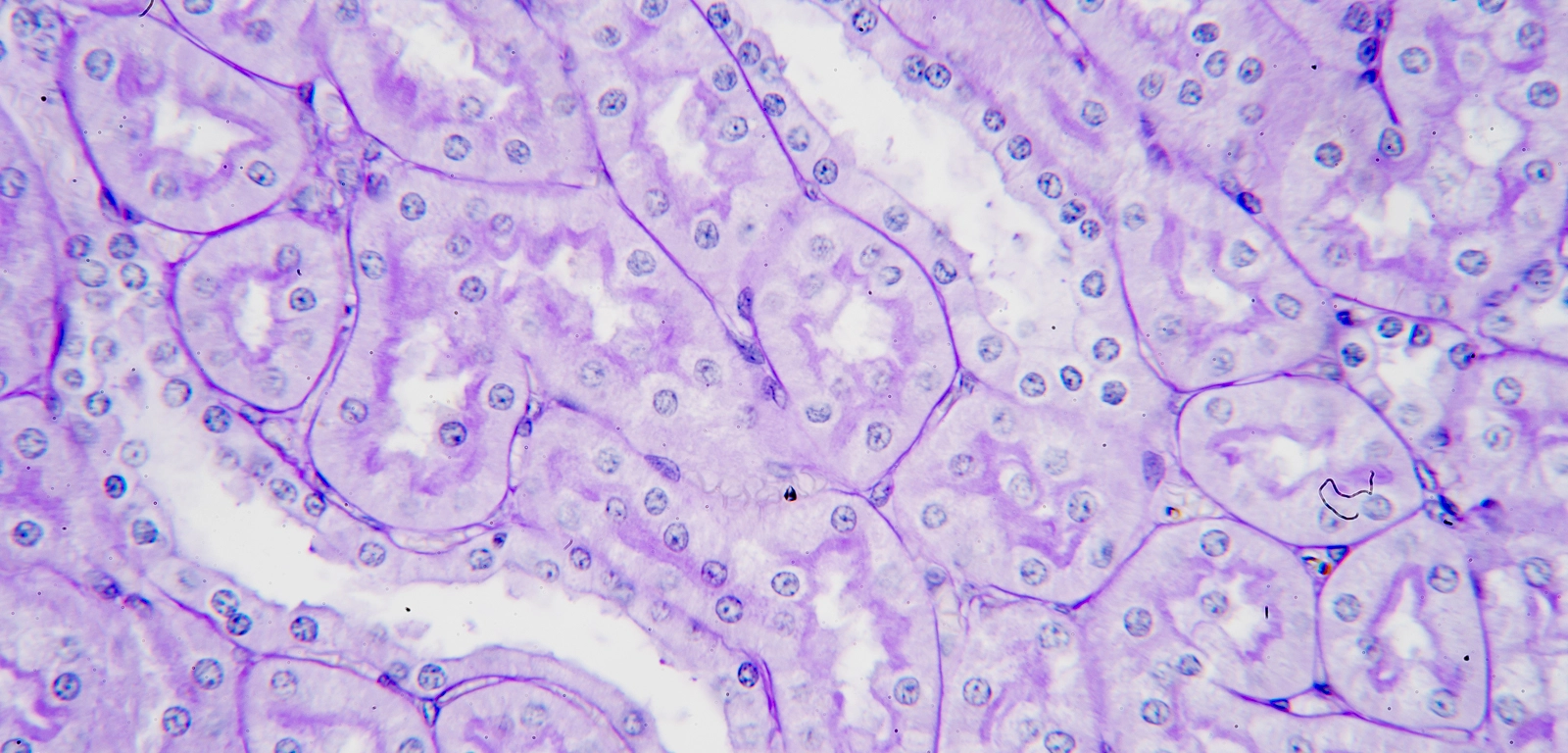
Simple Cuboidal
kidneys
secretion n absorption
Transitional Epithelium
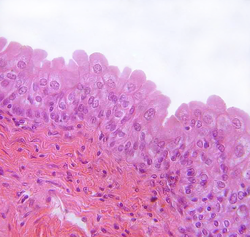
blocks diffusion
urinary bladder
Simple Columnar
secretion n absorption
digestive tract
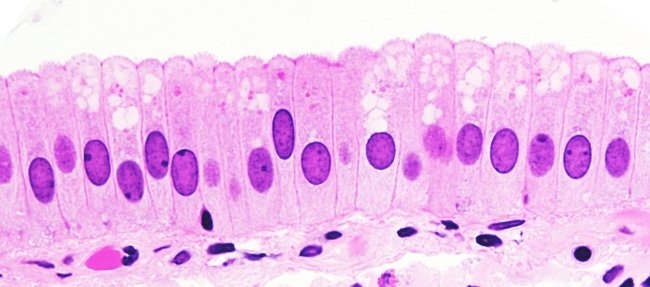
Ciliated
move particles out of body
respiratory tract

Stratified Squamous

Skin n Mouth
protection
Pseudostratified Columnar
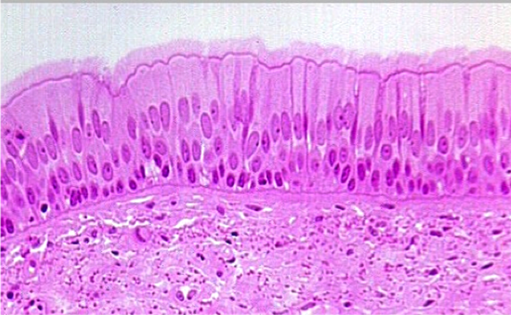
cilia-aided movement
lining air passages
Glandular

saliva
Secrete substances
Nervous
Spinal
send and receive signals from brain

vertebral foramen
Connective
Loose connective

membranes throughout body
Binds underlying organs to skin and to each other
adipose
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adipose_tissue_2-5b48c694c9e77c0037187836.jpg)
beneath skin
stores energy
Cartilage
Hylaline
covers end of joints

nose n respiratory
Elastic
allows organs to stretch

ear n larynx
Fribrocartilage
between vertebrae
to absorb

Dense Fibrous
ligaments n tendons
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_connective_tissue-56a09aee3df78cafdaa32ca1.jpg)
function in support
Bone tissue
protects soft tissues

bones
Blood tissue
fluid portion of body
supplying oxygen to cells nd tissues

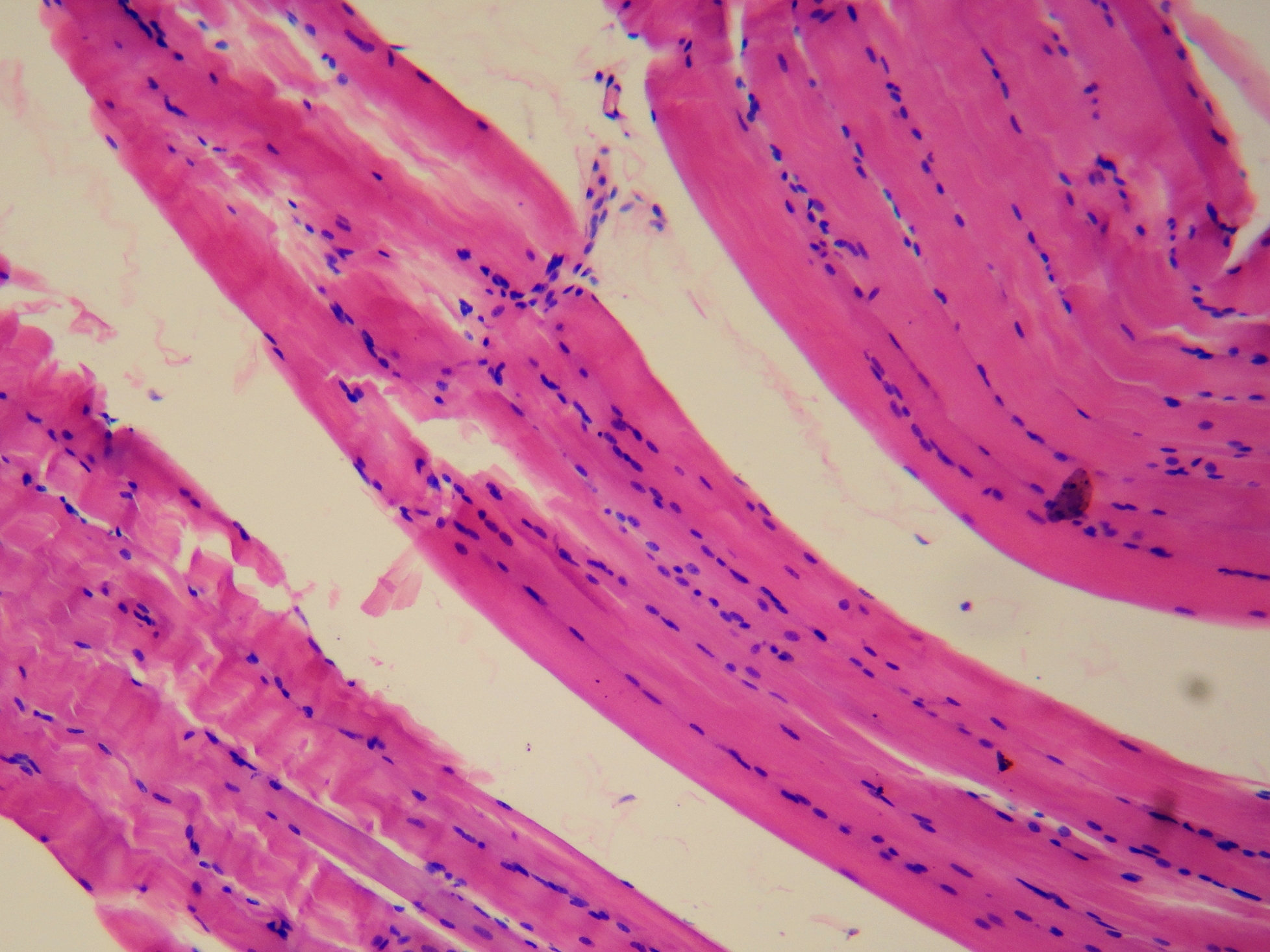
Muscle tissue
Cardiac

keep heart pumping
walls of heart
Skelatel

support n movement
walls of hollow visceral organs
Smooth
walls of hollow organs
maintaining and controlling blood pressure and flow of oxygen