TISSUE TYPES IN THE BODY
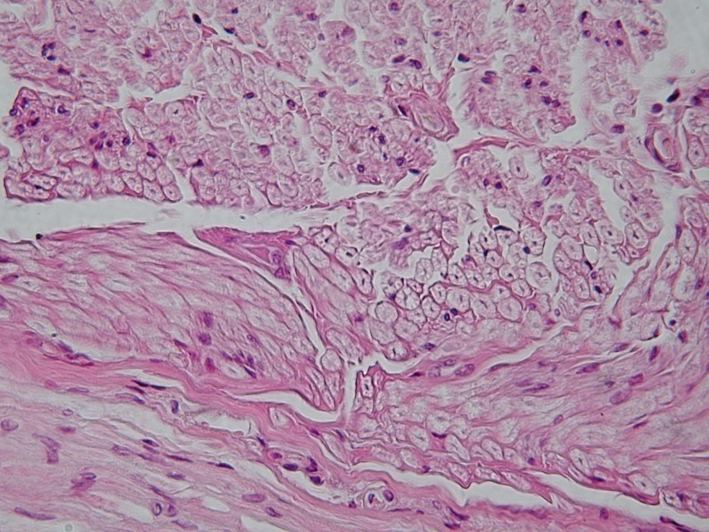
EPITHELIAL
PSEUDOSTRATIFIED COLUMNAR
LOOKS LIKE

Appear stratified, but just a single layer of cells, nuclei at different levels.
FOUND IN
Lining air passages and tubes of the reproductive system.
FUNCTIONS TO
Secretion and cilia-aided movement.
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS
FOUND IN
Air sacs of the lungs and walls of the capillaries.
FUNCTIONS TO
Diffusion and filtration.
LOOKS LIKE

Single layer of flat cells.
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL
LOOKS LIKE

Single layer of cubes
FOUND IN
Kidney, Tubules, and Ducts
FUNCTIONS TO
Secretion and absorption
SIMPLE COLUMNAR
LOOKS LIKE

Single layer of vertical columns.
FOUND IN
Digestive tract and uterus.
FUNCTIONS TO
Secretion and absorption.
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
LOOKS LIKE

Multiple layers of flat cells.
FOUND IN
Skin and mouth.
FUNCTIONS TO
Protection
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIUM
LOOKS LIKE
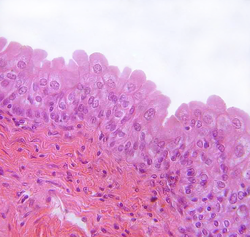
Group of cells that separates tissue.
FOUND IN
Urinary bladder
FUNCTIONS TO
Blocks diffusion (no leaking)
STRATIFIED COLUMNAR
LOOKS LIKE

FOUND IN
The male urethra and the ducts of some glands.
FUNCTIONS TO
Secrets and protects.
STRATIFIED CUBOIDAL
LOOKS LIKE
FOUND IN
Sweat glands , salivary glands, and the mammary glands.
FUNCTIONS TO
Protective tissue
GLANDULAR
FUNCTIONS TO
Makes up glands
FOUND IN
Forms the covering of all glands
LOOKS LIKE

CONNECTIVE
TISSUE
CARTILAGE
ELASTIC CARTILAGE
Found in external ear and larynx.

HYALINE CARTILAGE
covers end of joints, nose, and respiratory passages.

FIBROCARTILAGE
Tough, shock, absorbing. Found between vertebrae.

ADIPOSE TISSUE
Functions as a protective cushion, insulates to preserve body heat; stores energy.

FIBROUS CONNECTIVE TISSUE
functions in support including muscles to bones, ligaments
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_connective_tissue-56a09aee3df78cafdaa32ca1.jpg)
LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE OR AREOLAR TISSUE
Binds underlying organs to skin and to each other. Forms delicate thin membranes throughout the body.

BONE TISSUE
functions in the body, such as locomotion, support and protection of soft tissues, calcium and phosphate storage, and harboring of bone marrow.

BLOOD TISSUE
Has a fluid matrix, called plasma, and no fibers. Involved in the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide.

MUSCLE
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Involuntary controlled. Single nucleus. Found in the circulatory pump.
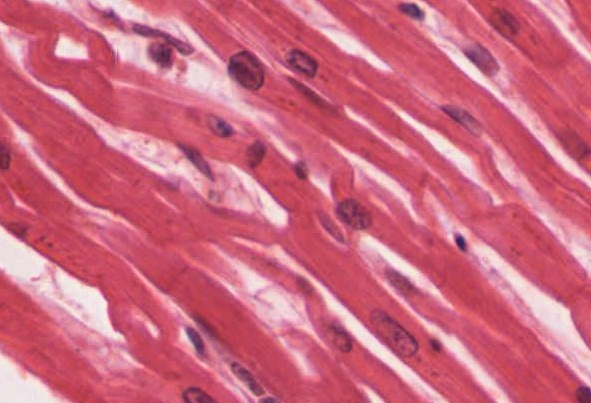
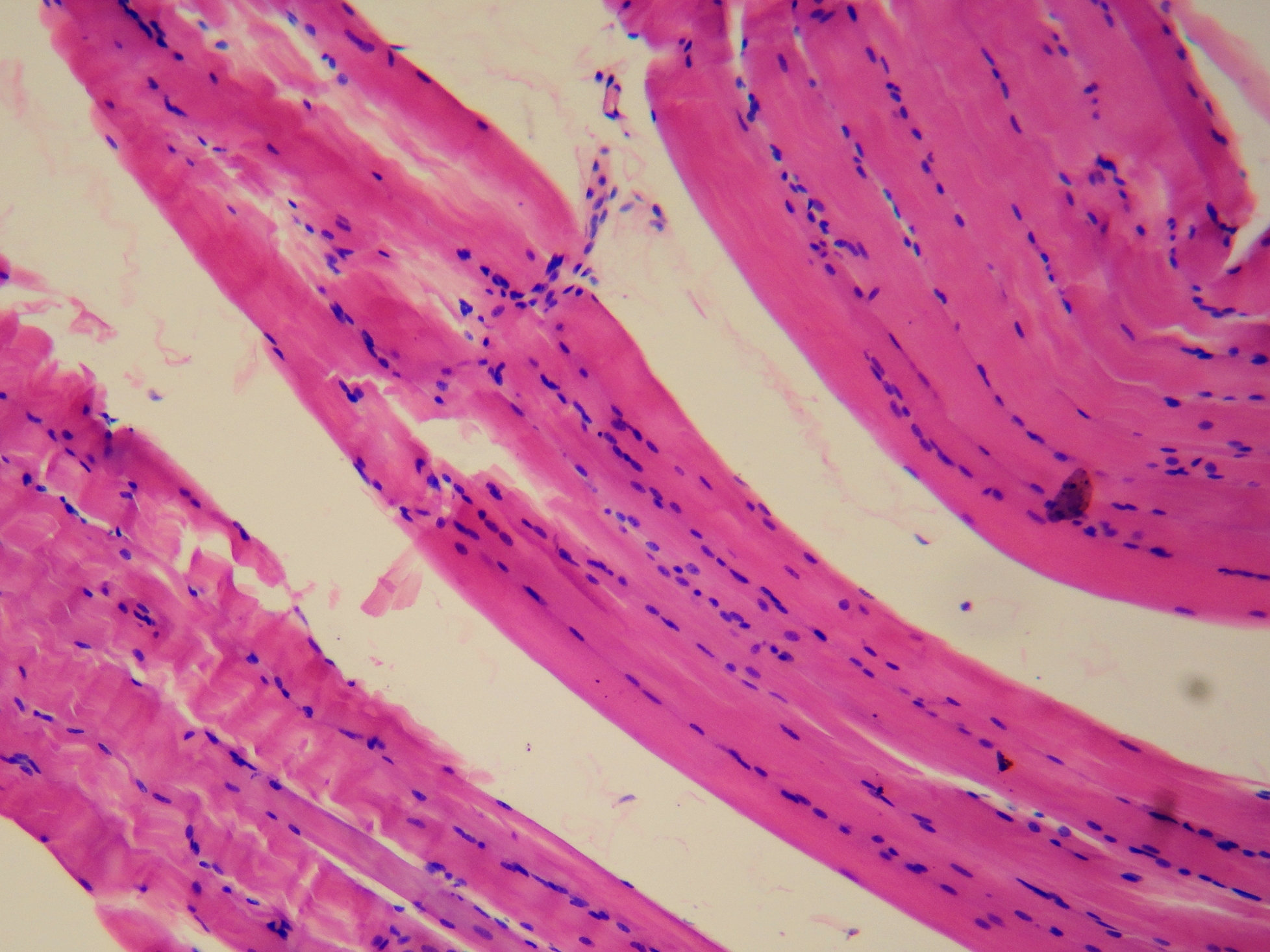
SKELETAL MUSCLE
Voluntary controlled. Attached to bones. Controls movement.

SMOOTH MUSCLE
involuntary controlled. Allows to direct eyeballs. Found in walls of stomach and uterus.
NERVES
NERVE TISSUE
MADE UP OF
NEURONS
FUNCTIONS TO
Produce action potentials and transmit signals.
FOUND IN
The spinal cord