Tissue Types of the Body
Epithelial
Simple Squamous

flat/thin
capillaries, alveoli, glomeruli, and other tissues where rapid diffusion is required
diffusion and filtration
Simple Cuboidal
Secretion and absorption
kidneys tubules, ducts and covering the ovaries

Simple Columnar
ecretion and absorption
digestive tract and uterus
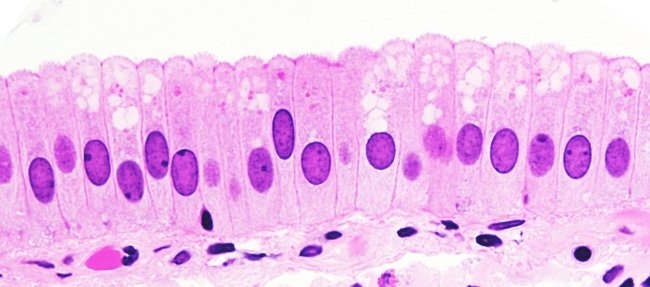
Stratified Squamous
protection
lining body cavities; skin and mouth

Pseudostratified Columnar

lining air passages and tubes of the reproductive system
Secretion and cilia-aided movement
Transitional Epithelium
urinary bladder
Blocks diffusion
Glandular Epithelium
specialized to secrete substances
They make up the glands
saliva

Stratified Cuboidal
salivary glands, kidney tubules, sweat glands
secretion and protection
Stratified Columnar
protection and mucous secretion

conjunctiva inside the eyelids and areas of tissue transition
Connective
Fibrous Dense Connective Tissue
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dense_irregular_conn_tissue-5b68c5db46e0fb0050b3a01b.jpg)
dermis, tendons, ligaments
support
Loose Connective Tissue or Areolar Tissue

throughout body
Binds underlying organs to skin and to each other
Fibrocartilage
shock absorbing

between vertebrae
Bone Tissue (Osseous)
skeleton
locomotion, support and protection

Adipose Tissue (fat)
throughout body
Protective cushion
insulation to preserve body heat
Stores energy
Blood Tissue
blood vessels
transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide

Elastic cartilage
shaping the folds which efficiently channel sound waves towards the inner ear
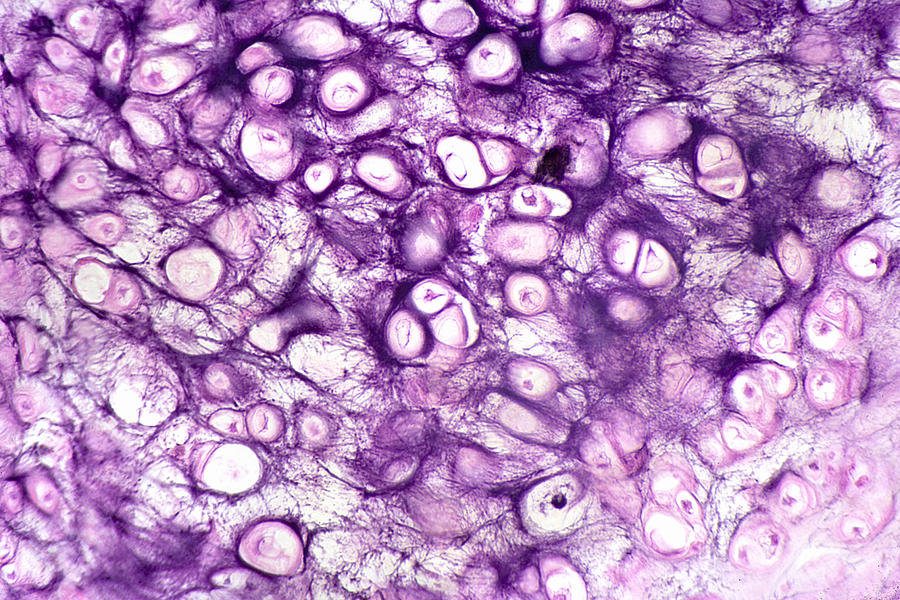
External Ear and Larynx
Hyaline cartilage

helps hold the body together
covers ends of joints, nose and respiratory passages, serves as padding
Muscle
Skeletal

between bones
uses tendons to connect the epimysium to the periosteum, or outer covering, of bone
Cardiac
performs coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood through your circulatory system
heart

Smooth
contract to push food through your body
walls of hollow organs like your intestines and stomach

Nervous Tissue (spinal cord)
brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
coordinating and controlling many body activities