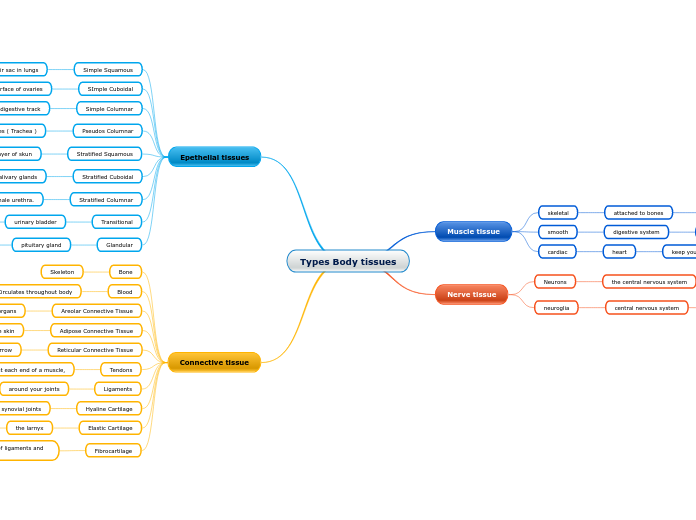
Types Body tissues
Muscle tissue
skeletal
attached to bones
move and perform daily activities
smooth
digestive system
helps with digestion and nutrient collection
cardiac
heart
keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements
Nerve tissue
Neurons
the central nervous system
maintaining homeostatic control and immune surveillance in the nervous system.
neuroglia
central nervous system
maintaining homeostatic control and immune surveillance in the nervous system.
Epethelial tissues
Simple Squamous
Air sac in lungs
facilitate diffusion of gases and small molecules.
SImple Cuboidal
surface of ovaries
secretion and absorption
Simple Columnar
digestive track
protection
Pseudos Columnar
Air passages ( Trachea )
elp trap and transport particles brought in through the nasal passages and lungs.
Stratified Squamous
outer layer of skun
protection
Stratified Cuboidal
lining of the ducts of the salivary glands
rotect areas such as ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
Stratified Columnar
conjunctiva, pharynx, anus, and male urethra.
providing protection and secretion.
Transitional
urinary bladder
stretch readily in order to accommodate fluctuation of volume of the liquid in an organ
Glandular
pituitary gland
to produce and release different secretory products
Connective tissue
Bone
Skeleton
Blood
Circulates throughout body
Areolar Connective Tissue
Binds skin to internal organs
he support and binding of other tissues.
Adipose Connective Tissue
Layer beneath the skin
to collect, store and then release lipids.
Reticular Connective Tissue
Suthe kidney, the spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow
form a stroma and provide structural support,
Tendons
at each end of a muscle,
serves to move the bone or structure.
Ligaments
around your joints
serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
Hyaline Cartilage
in the synovial joints
assists the motion of joints.
Elastic Cartilage
the larnyx
provides strength, and elasticity
Fibrocartilage
the intervertebral disks and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons
the tough material of the intervertebral disc