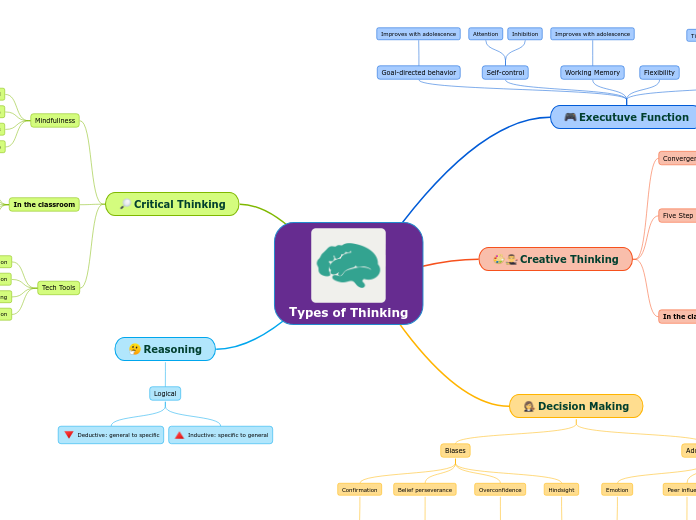
Types of Thinking
Executuve Function
Goal-directed behavior
Improves with adolescence
Self-control
Attention
Inhibition
Working Memory
Improves with adolescence
Flexibility
In the classroom
Time-management
Minimize distractions
Self-regulation
Creative Thinking
Convergent vs. Divergent
Schools favor convergent, but creative thinkers are divergent
Five Step Process (not always linear)
Preparation
Incubation
Insight
Evaluation
Elaboration
In the classroom
Think flexibly
Take risks
Community role models
State of FLOW
Build confidence
Honor diversity
Decision Making
Biases
Confirmation
eg, web searches
Belief perseverance
Rigid thinking
Overconfidence
Very common in children
Hindsight
20/20
Adolescents
Emotion
Lack of inhibition
Peer influence
Immediate gratification
Analytical vs. Experiential
Usually a mix of both
Critical Thinking
Mindfullness
Open mind
Process > Outcome
Ask good questions
Alert and flexible
In the classroom
Ask "how" and "why"
Multiple "right" answers
Evaluate evidence
Explore all angles
Large and small discussion
Tech Tools
Digital collaboration
Semantic organization
Dynamic modeling
Info interpretation
Reasoning
Logical
Deductive: general to specific
Inductive: specific to general