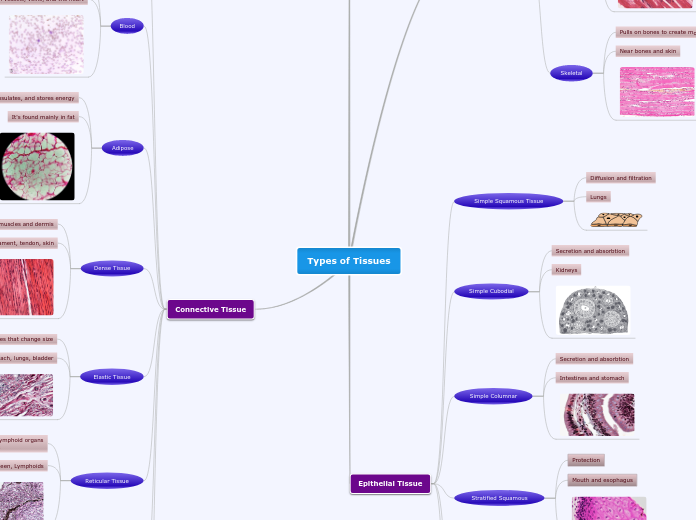
Types of Tissues
Muscle Tissue
Smooth
To contract and expand in hollow organs
Digest, move blood through the body
In hollow organs like the stomach
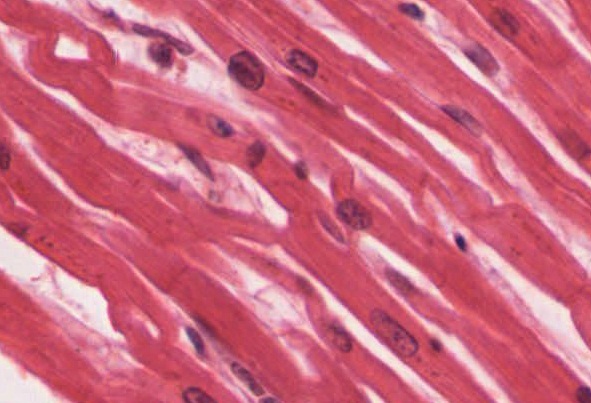
Cardiac
Helps the heart pump blood to the body
The heart
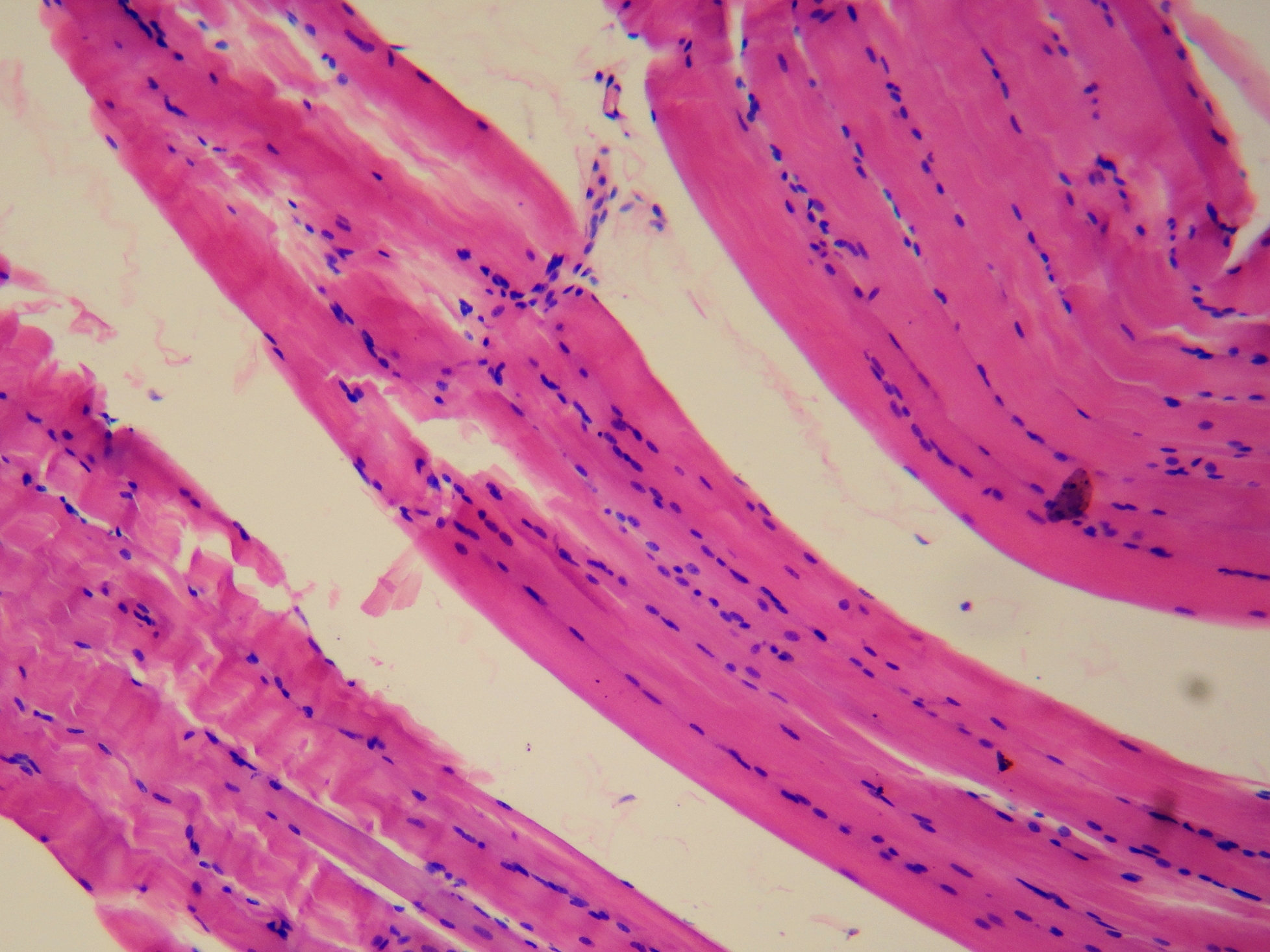
Skeletal
Pulls on bones to create movement
Near bones and skin

Epithelial Tissue
Simple Squamous Tissue
Diffusion and filtration
Lungs
Simple Cubodial
Secretion and absorbtion
Kidneys

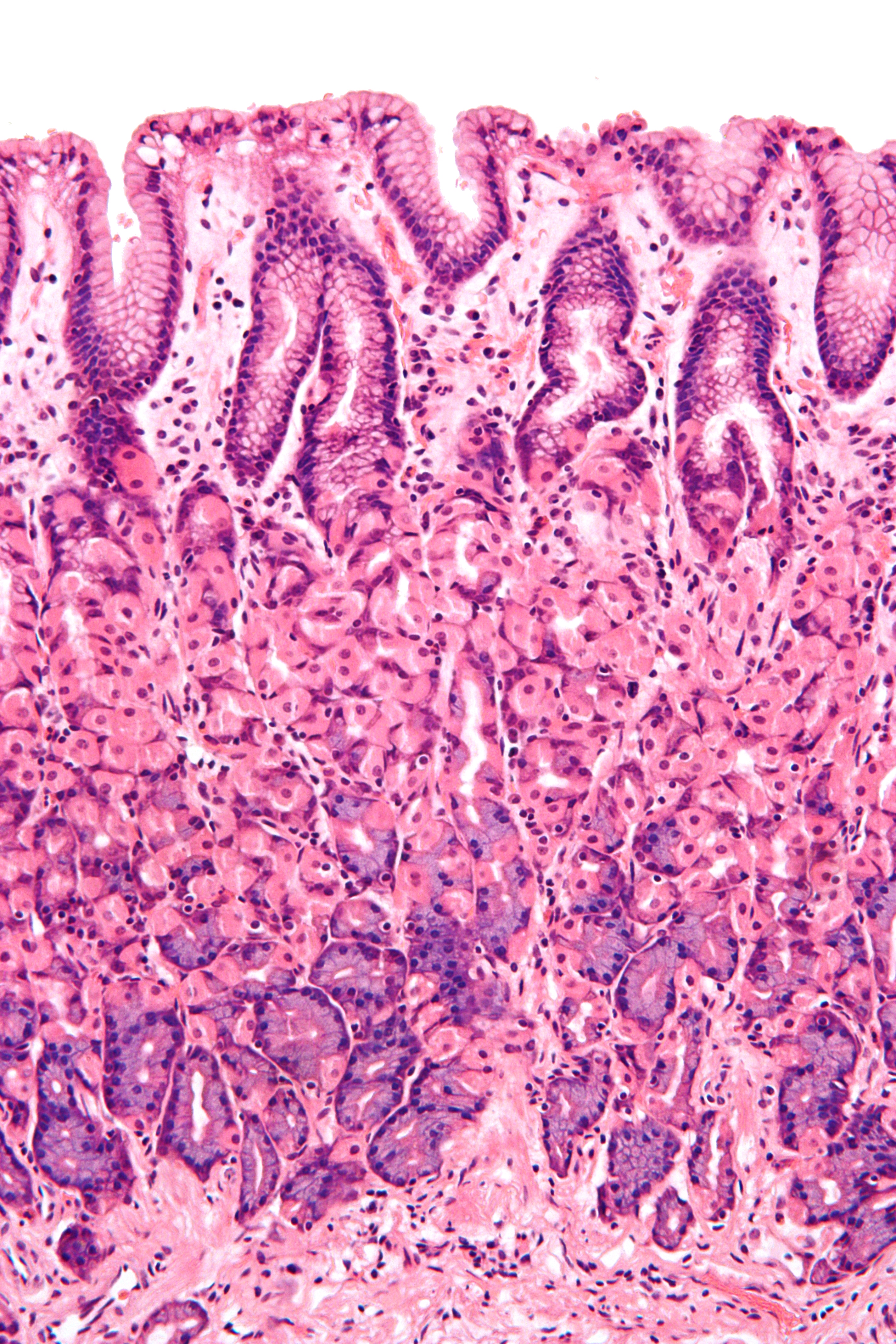
Simple Columnar
Secretion and absorbtion
Intestines and stomach

Stratified Squamous
Protection
Mouth and esophagus

Stratified Cubodial
Secretion and absorbtion
Salivary glands and sweat glands
Pseudo Stratified Columnar
Secretion and cilia aided movement
Lining air passageways and reproductive tubes
Nervous Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Creates neurons
Send electrical signals to the body
Neurons
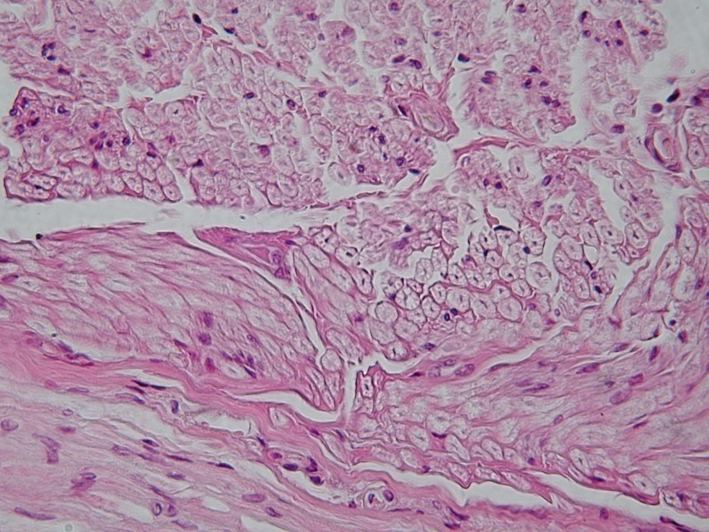
Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Protects the body and holds the organs together
Found in fat and every organ system in the body

Blood
Carries products throughout the body to the cells
It's found in vessels, veins, and the heart

Adipose
Protects the body, insulates, and stores energy
It's found mainly in fat

Dense Tissue
Forms muscles and dermis
Ligament, tendon, skin
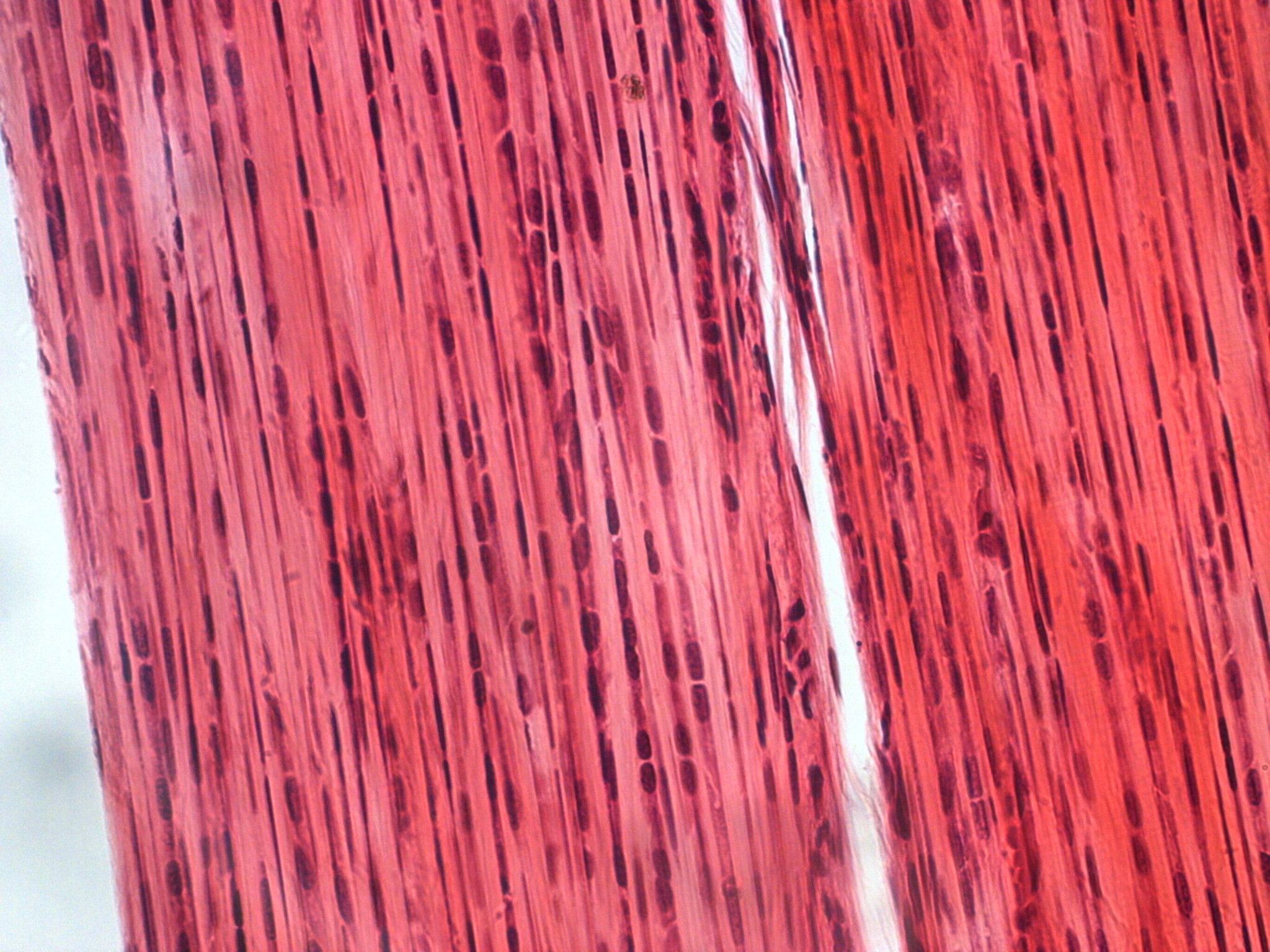
Elastic Tissue
Supports structures that change size
Stomach, lungs, bladder

Reticular Tissue
Supports blood cells and lymphoid organs
Produces white blood cells
Spleen, Lymphoids

Cartilage
Forms support for body and covers the ends of bones
Ears and Nose

Bone
Protects and supports organs
Bones