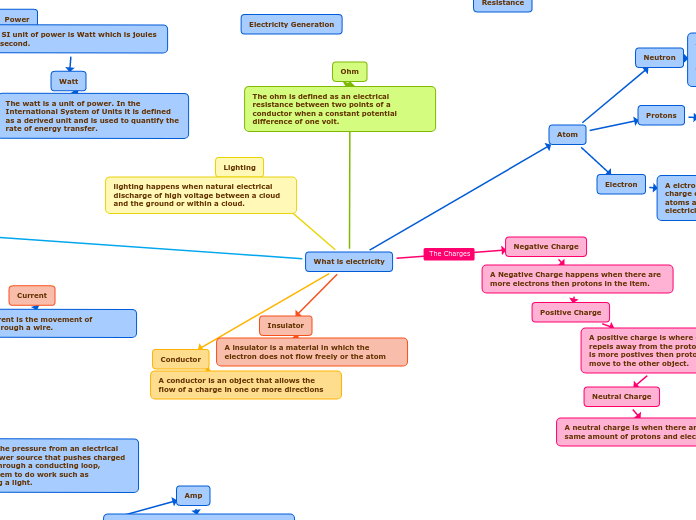
What is electricity
Negative Charge
A Negative Charge happens when there are more electrons then protons in the item.
Positive Charge
A positive charge is where everything repels away from the proton or when there is more postives then protons give up and move to the other object.
Neutral Charge
A neutral charge is when there are the same amount of protons and electrons.
Lighting
lighting happens when natural electrical discharge of high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud.
Ohm
The ohm is defined as an electrical resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of one volt.
Parallel Circuit
A parallel circuit has two or more paths for current to flow through. Voltage is the same across each component of the parallel circuit. The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source.
Series Circuit
The current in a series circuit goes through every component in the circuit. Therefore, all of the components in a series connection carry the same current. A series circuit has only one path in which its current can flow.
Conductor
A conductor is an object that allows the flow of a charge in one or more directions
Insulator
A insulator is a material in which the electron does not flow freely or the atom
Atom
Neutron
A neutron is about the same mass as a proton but without an electric charge, present in all atomic nuclus except those of ordinary hydrogen. and is found in the nuclus
Electron
A elctron is found in the nuclus with a charge of negative electricity, found in all atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity in solids.
Protons
A proton is a with a positive electric charge, and is found in the nuclus with the neutrons.
Static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material.
Friction
Friction is the resistance to motion of one object moving relative to another
Power
The SI unit of power is Watt which is joules per second.
Watt
The watt is a unit of power. In the International System of Units it is defined as a derived unit and is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer.
Circuit
An electric circuit includes a device that gives energy to the charged particles constituting the current, such as a battery or a generator.
Voltage
Voltage is the pressure from an electrical circuit's power source that pushes charged electrons through a conducting loop, enabling them to do work such as illuminating a light.
Volt
The volt is the derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta
Amp
An ampere is the unit used to measure electric current.
Amperage
The strength of an electric current in amperes.
Battery
A battery is many things it can be big and heavey for a v12 car or it can be something to make your toy work but the science behind it is A device containing an electric series of electric cells storing chemical energy that can be converted into electrical power usually in the form of direct current.
Repulsion
Repulsion is like a force bewteen 2 thing like when you use a postive magnet agensit a postive megnet the repulse
Resistance
Attraction
Attraction is when like for exsample a postive agasit a negative charge will attrac like with a magnet on a frige