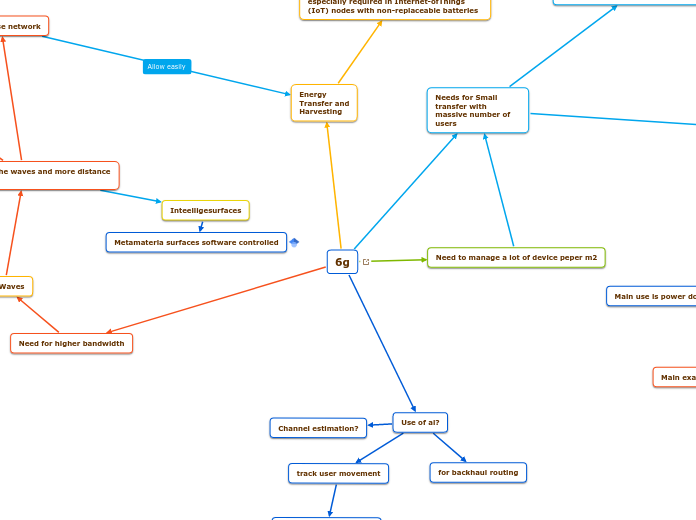
Inteelligesurfaces
Metamaterla surfaces software controlled
Low phase noise local oscilator
Ongoing research
https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/10.1038/s41566-021-00790-2
Phase noise resistant modulation
NOMA
Power domain NOMA has recently been excluded from the 3GPP standard because of many problems related to its low performance compared to other competitive methods, receiver complexity, security vulnerability, and signaling overhead. To address these problems, we have developed new types of NOMA that can be found in this paper https://rs-ojict.pubpub.org/pub/tphonik9/
In downlink NOMA, a user doesn’t need to know the channel of anyone else since all signals reach the user over the same channel. However, the user must know the modulation and coding scheme of the co-users.
Fucked up with mimo. The way noma is interesting in mimo situation is when we have multiple users at the same time in the Line of sight of the antenna. In this case, the multiple antennas acts like a single one and NOMA can be better in this case
Main examples are for 2 or 4 users
Main use is power domain NOMA
6g
The World's Oceans
- 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water
- The oceans contain 97% of the earth's water
- All oceans and seas are actually one continuous body of water
- Oceanographers are scientist who study the ocean and its processes.
Need to manage a lot of device peper m2
Needs for Small transfer with massive number of users
Massive mimo, spacial multiplexing
New modulation schemes
SDMA
SDMA based on MU–LP
Although MU–LP is suboptimal for the multi-antenna BC, it achieves a near-capacity performance when CSIT is perfect and the user channels are nearly orthogonal with similar channel strengths or similar long-term signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) [8]. SDMA based on MU–LP1 is therefore an integral part of numerous 4G and 5G transmission schemes such as multi-user MIMO (MU–MIMO), networked MIMO, coordinated multi-point (CoMP), massive MIMO, and millimeterwave (mmWave) MIMO. Linear precoding schemes, such as zero-forcing beamforming (ZFBF) [8], minimum mean square error (MMSE), regularized ZFBF (R-ZF) [6], block 1 In the rest of the paper, for simplicity, we use “SDMA” when we want to refer to “SDMA based on MU–LP”. 4 diagonalization (BD) [9], maximum ratio transmission (MRT) [10], and maximum signal-to-leakage-and-noise ratio (SLNR) transmission [11] have been extensively used in practical
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.03192.pdf
Rate multiplexing ?/RSMA?
https://sci-hub.hkvisa.net/10.1109/vtc2020-fall49728.2020.9348672
good results in papers
Seems to be lobbied ?
FBMC
Energy
Transfer and
Harvesting
Very lowpower communications is especially required in Internet-ofThings (IoT) nodes with non-replaceable batteries
Need for higher bandwidth
mmWaves
300ghz
Phase noise
lower reach of the waves and more distance related issues
More dense network
multiple antennas beamforming
Needs for high precision positionning
hybrid beamforming
How to detect position of users
Use of ai?
Channel estimation?
track user movement
Use of multi antennas ?
for backhaul routing