door madhav kapoor 5 jaren geleden
1533
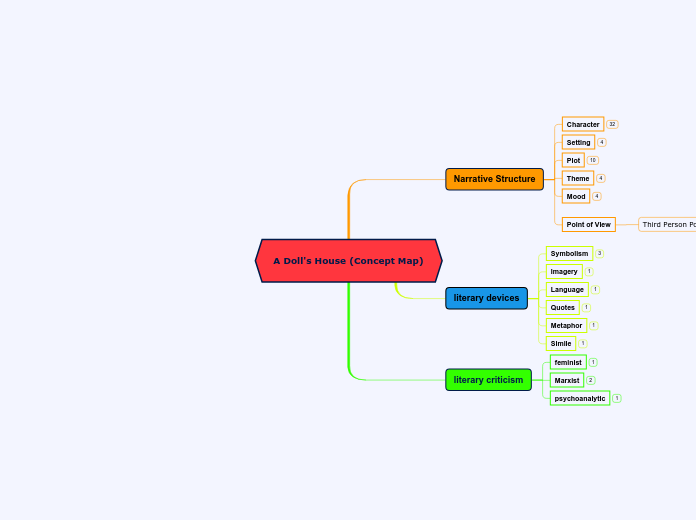
A Doll's House (Concept Map)
door madhav kapoor 5 jaren geleden
1533

Meer zoals dit
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
An adverb is used to describe a verb, but it can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Adverbs normally help paint a fuller picture by describing how something happens.
The intensifiers strengthen adverbs adjectives and adverbs and down- toners make them weaker.
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
Interrogative pronouns are used in questions. Although they are classified as pronouns, it is not easy to see how they replace nouns. Who, which, what, where, and how are all interrogative pronouns.
Reciprocal pronouns are used for actions or feelings that are reciprocated. The reciprocal pronouns are each other and one another.
A reflexive pronoun ends with ...self or ...selves and refers to another noun or pronoun in the sentence (usually the subject of the sentence). The reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, himself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Demonstrative pronouns are used to demonstrate (or indicate). This, that, these, and those are all demonstrative pronouns.
Possessive pronouns are used to show possession. The possessive pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Ibsen has used the characters names in the play which justified that the play is written in third person point of view.
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
The mood throughout is stressed. Nora always lives with the fear that her husband, Torvald might find out about the loan she took for his treatment. Nora is never at peace due to the fact that Krogstad knows about her secret.
In the play, Nora appears as an innocent women who is oblivious of the struggles in life but in reality Nora has the intelligence to get a loan from Krogstad to save Torvald's life.
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
Obtaining wealth has been a major aim of Torvald and Nora as they struggle to go to italy and have always dreamt of a lavish life.
The play is based on the theme of marriage which is supposed to be a relationship based on trust and respect. Initially, Nora ignored trivial insults by Torvald and tried to save their marriage by obeying him. However, Nora revolts at the end and leaves Torvald.
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
Nora decides to leave her husband and children as she looked at Torvald as a strange man.
Nora realizes that she has been controlled by Torvald for her whole life. Torvald convinces Nora that he wil change his way but Nora plans to leave Torvald to lead a better life.
Torvald finally reads the letter and yells at Nora. She is surprised to find the true colours of Torvald and feels as if she was being controlled like a doll since marrige.
Krogstrad, who gave Nora the loan,came to tell her that he will tell Torvald how Nora got the money if she does not convince Torvald to not fire Krogstad. When Krogstad finds out that Torvald fired him, he places a letter in Torvalds mailbox stating that Nora forged illegal signature to get a loan. Nora tries to prevent Torvald from opening the mailbox and asks him to help her with dancing. Mrs.Linde and Krogstad start to get back together again.
The play begins in a furnished living room where one of Nora's school friends named Mrs.Linde comes to meet Nora. During the conversation Mrs.Linde talks about how much harder is her life than Nora's life. Nora starts to tell Mrs.Linde how she illegally saved Torvalds life.
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
A furnished living room is a great setting in the play because it is a cozy place to spend time with family on a Christmas Eve.
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.
Ivar
Emmy
Bobby
Wealthy person
Suffering from tuberculosis
In love with Nora
Fired from Torvald
Forged signatures
Loves Mrs.Linde
Looking for a job
Widow
Nora's school friend
Bank Manager
Nora's husband
Father of three children
Protective
Torvald treats Nora as her father would, he also makes sure to control Nora's macoroon eating habbit and protect her from any type of danger.
About
Mother of three children
Torvald's wife
Intelligent
Nora is mistaken to be a irresponible women with no knowledge of bank loans and finance, however, she manages to forge her fathers signature to get approval for the loan.
Greed
For the greed of money, Nora was ready to forge her father's signatures to obtain 250 pounds.