door KELLEN SUN 3 jaren geleden
246
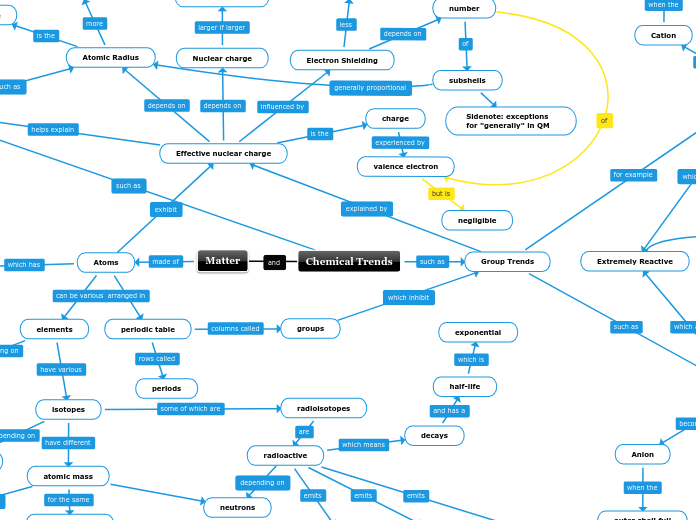
Chemical Trends
door KELLEN SUN 3 jaren geleden
246

Meer zoals dit
increases
an electron
bond
picometer
Sidenote: exceptions for "generally" in QM
electrons
Coulomb's Law
atomic mass
same element
neutrons
radioisotopes
radioactive
gamma radiation
beta radiation
alpha radiation
decays
half-life
exponential
neutron count
Electron
clouds of uncertainty
shells
subshells
cloverleaf
dumbbell
sphere
heisenberg uncertainty principle
momentum
position
same time
-1
Neutron
no charge
nucleus
centered in atom
Proton
+1
elementary charge
smallest possible charge
positively charged
diagrams
Conceptualization
properties, trends, etc
Stable shell
Non metals
outer shell full
Metals