door Andrew Bajana 5 jaren geleden
991
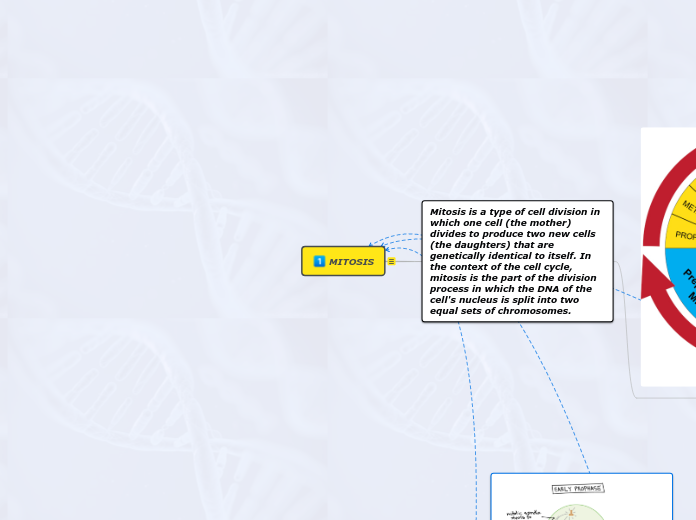
MITOSIS
Mitosis is a critical process in cell division where a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells. This process is vital for growth, asexual reproduction, and the repair and replacement of tissues in multicellular organisms.