door Vanessa Sgambelluri 5 jaren geleden
793
Molecular Genetics
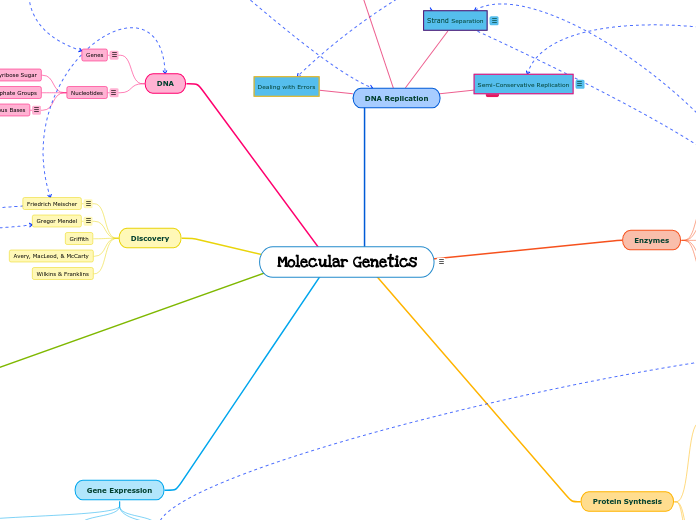
door Vanessa Sgambelluri 5 jaren geleden
793

Meer zoals dit
Connection from Base Pair Mutations - Substitution, Insertion, Deletion, and Inversion: Examples of base pair mutations are...
Connection from Complementary Base Pairings - Inversion: When two adjacent bases trade places, or DNA sequence becomes reversed, this is called...
Connection from Complementary Base Pairings - Deletion: The removal of a base pair or larger coding region from a DNA Sequence is called...
Connection from Complementary Base Pairings - Insertion: The addition of a base pair or a larger coding region to a DNA Sequence is called...
Connection from Complementary Base Pairings - Substitution: The replacement of one base pair in a DNA Sequence by another base pair is called....
Connection from Causes - Spontaneous Mutation: Mutations can happen spontaneously, which arise from inaccurate DNA replication. This is called...
Connection from Causes - Induced Mutation: Mutations can also be caused by an environmental agent. This is called...
Connection from Induced Mutations - Chemical Mutagen: When an environmental agent directly changes the DNA within a cell, this is known as a...
Connection from Replication Fork - Replication Bubble: The replication fork causes the separating of DNA in both directions, in which an opening is produced. This opening is known as the...
Connection from Replication Origin - Helicase: At this point, the following enzyme functions...
Connection from Strand Separation - Helicase: Enzyme that causes strand separation is...
Connection from Strand Separation - SSBs: During strand separation, the SSBs prevent the parent DNA strands from annealing and keep them separated.
Connection from Semi-Conservative Replication - Replication Origin: Semi-Conservative Replication starts at the ...
Connection from Eukaryotic Cells - DNA Replication: In this cell, this process takes place...
Connection from Hereditary Molecule - Fred. Meischer: The man who examined this molecule further was...
Focus Question: What are the fundamental processes and errors that take place in Eukaryotic Molecular Genetics?
BY: VANESSA SGAMBELLURI
Connection from Post-Translational - Processing, Chemical Modification, and Degradation: In this regulation measure, the availability of functional proteins is limited through the following processes...
Connection from Translational - Poly(A) Tail: In this regulation process, the length of the poly(A) tail is changed.
Connection from Post-Transcriptional - Alternative Splicing: An example of post-transcriptional regulation is...
Connection from Transcriptional - Chromatin Remodelling Complex and Metylation: Two examples of transcriptional regulation are...
Connection from Nonsense Mutation - Stop Codon: This mutation results in a premature...
Connection between Point Mutation - SNP: A change in a single nucleotide within a gene can cause a difference in the DNA between individuals, known as...
Connection from Gregor Mendel - Hereditary Molecule: Proposed a "factor" which he called a...
Connection from Fred. Meischer to DNA: Collected pus to discover...
Connection from Nucleotides - Deoxyribose Sugar, Phosphate Groups, and Nitrogenous Bases: Consists of...
Connection from Nitrogenous Bases - Purines & Pyrimidines: Examples of Bases include...
Purine & Pyrimidines
Connection from Purines & Pyrimidines - Complementary Base Pairings: A purine always pairs with a pyrimidine! This makes up what we know as...
Connection from Genes - Eukaryotic Cells: Gene function can differ in the two cells; EUKARYOTIC & Prokaryotic
Connection from Genetic Coding - Codon: Codons provide a mechanism for Genetic Coding.
Connection from Genetic Coding - AT, GC: Genetic Coding is dependent on the DNA alphabet, which is consistent of A, T, G, and C.
Connections from Codons - Start and Stop Codon: Specific codons that assist in the process of translation are...
Stop Codon
Start Codons
Connection from Central Dogma - Transcription: Genetic information flows from DNA to RNA
Connection from Central Dogma - Translation: Genetic information flows from RNA to Proteins
Connection from Translation to Initiation, Elongation, and Termination: These are the first, second, and third steps of translation.
Connection from termination - Stop Codon: The codon that ends translation and signals the termination of the polypeptide chain is...
Connection from Initiation to Start Codon: The codon that begins translation and initiates the formation of the polypeptide chain is...
Connection from Transcription to Initiation, Elongation, and Termination: These are the first, second, and third steps of transcription.
Termination
Connection from Termination - Termination Sequence: Termination occurs when RNA Polymerase recognizes the...
Termination Sequence
Connection from Termination Sequence - RNA Polymerase: The enzyme that detects the termination sequence to terminate transcription is called...
Elongation
Initiation
Connection from Initiation - Promoter: Initiation occurs at the promoter.
Promoter
Connection from Promoter - TATA Box: The TATA Box is located on the promoter.
TATA Box
Connection from TATA Box - RNA Polymerase: The TATA Box allows for the binding of...
RNA Polymerase
Connection from RNA Polymerase - Building Complementary Strands: Once RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, DNA's double helix will open. Then, the enzyme begins to build a complementary single-stranded RNA molecule.
Building Complementary Strands
Connection from Building Complementary Strands - DNA Replication Building Complementary Strands: Complementary strands are built using a DNA Template strand in both DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis.
Connection to mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA: Different types of RNA include...
Connection to Nucleotides and Single-Stranded: RNA is single-stranded and contains nucleotides
Connection from Nucleotides - Ribose Sugar, Nitrogenous Bases, and Phosphate Groups: These parts make up RNA's nucleotides.
Phosphate Groups
Nitrogenous Bases
Connection from Nitrogenous Bases - Purines & Pyrimidines: Purines & Pyrimidines are examples of nitrogenous bases.
Purines & Pyrimidines
Connection from Purines & Pyrimidines - A, U, G, C: RNA nucleotides contain these four nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C). These form complementary base pairs with each other (UA, GC).
A, U, G, C
A, U, G, C - Genetic Coding: A, U, G, and C make up the RNA alphabet, which is important to...
Ribose Sugar
Connection from rRNA - Ribosomes: rRNA makes up...
Ribosomes
Connection from tRNA - Anticodon: Each tRNA contains a set of three nucleotides called an...
Connection from tRNA - Translation: The tRNA molecule is required by the ribosome through the following process so that one amino acid at a time can be assembled into a polypeptide chain.
Anticodons
Connection from mRNA - Precursor mRNA: The initial eukaryotic mRNA molecule that is made through transcription is this...
Connection from mRNA - Modified mRNA: The modified eukaryotic mRNA molecule that is made through transcription and can now exit the nucleus to reach the ribosome is this...
Modified mRNA
Connection from Modified mRNA - Poly(A) Tail: This is one modification that is made to the precursor RNA, where a chain of 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides are added to the 3' end.
Connection from Modified mRNA - 5' Cap: This is another modification that is made to the mRNA, where a sequence of seven G's are added to the start of the precursor mRNA.
Connection from Modified mRNA - mRNA Splicing: This is another and the final modification that is made to the precursor mRNA, where the introns are signalled to be removed.
mRNA splicing
Connection from mRNA Splicing - Introns: This process removes introns from precursor mRNA.
Small Ribonucleoprotein (snRNPs)
Alternative Splicing
5' Cap
Poly(A) Tail
Precursor mRNA
Connection from Precursor mRNA - Introns and Exons: This molecule includes both introns, non-coding sequences, and exons, coding sequences.
Exons
Introns
Connection from RNA Primase - RNA Primer: A replication enzyme producing...
Connection from RNA Primer - DNA Polymerases: When the RNA Primer is in place, DNA Polymerases, specifically DNA Polymerase III, allows for DNA nucleotides to become added to this primer.
DNA Polymerases
Connection from DNA Polymerases - I, II, and III: All three enzymes, DNA Polymerase I, DNA Polymerase II, and DNA Polymerase III are crucial to the process of DNA Replication.
Connection from DNA Polymerases - Building Complementary Strands and Dealing with Errors: DNA Polymerases' two significant functions include to assemble nucleotides into new DNA strands and to proofread and repair replication errors to DNA molecules.
I,II,III
Connection between Helicase - Replication Fork: As the helicase enzyme works, it forms a point of separation between the two parent DNA strands, called a ...