door Tedla Tyndall 5 jaren geleden
227
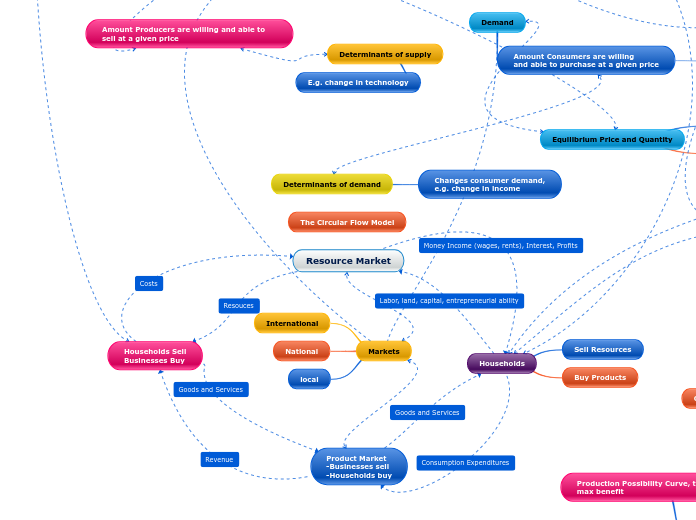
Resource Market
door Tedla Tyndall 5 jaren geleden
227

Meer zoals dit
Lowers with recession
Fed Gov't begins Fiscal SPending
As G decreases, AD decreases
As G increases, AD increase
Federal Reserve lowers interest rate
Multiplier effect
money supply shrinks and interest increases
investment spending decreases, AD decreases
Inflation decreases
this increases the money supply, interest rate falls
investment spending increases, AD increases, GDP increases
creates surplus
For demand-pull inflation
Creates deficit
for use in recessions