door Álvaro Alcaine Rueda 7 jaren geleden
425
UNIT 1 - TENSES
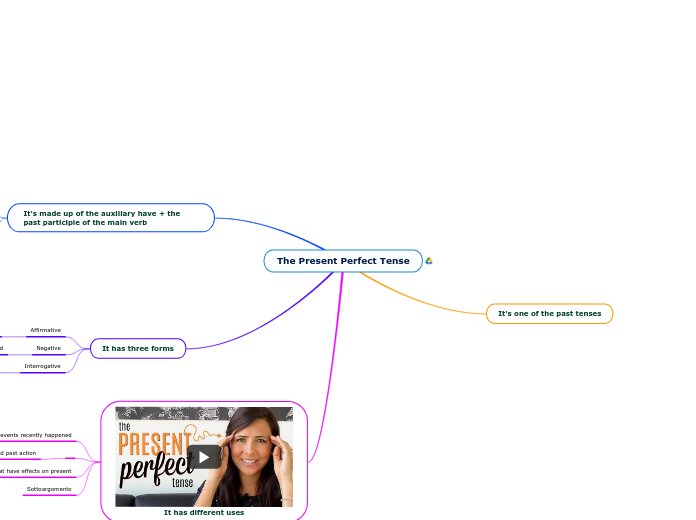
The document explains the use of various tenses, focusing primarily on the future perfect, past simple, and present simple tenses. The future perfect tense is used to describe actions that will be completed at a certain point in the future, often accompanied by temporary expressions.