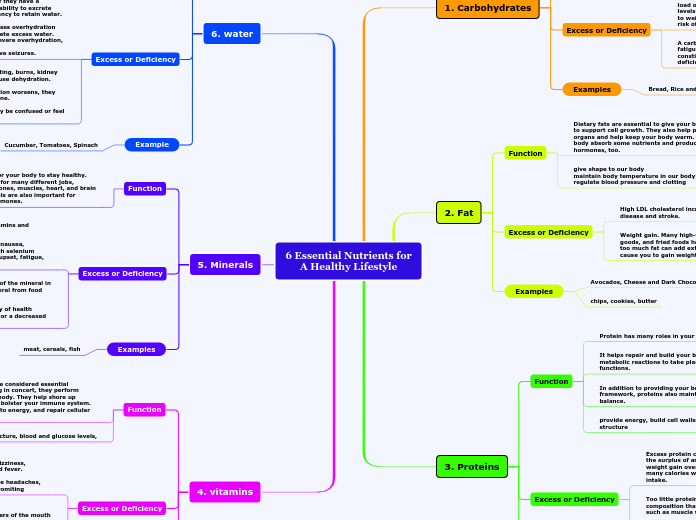
6 Essential Nutrients for
A Healthy Lifestyle
1. Carbohydrates
Function
They provide you with energy for daily tasks and are the primary fuel source for your brain’s high energy demands.
Fiber is a special type of carb that helps promote good digestive health and may lower your risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Excess or Deficiency
Excess carbohydrate intake places a large metabolic load on the body. When the body constantly has high levels of blood sugars to deal with over time, this leads to weight gain, poor metabolic health and an increased risk of heart disease.
A carbohydrate-deficient diet may cause headaches, fatigue, weakness, difficulty concentrating, nausea, constipation, bad breath and vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Examples
Bread, Rice and Cereal
2. Fat
Function
Dietary fats are essential to give your body energy and to support cell growth. They also help protect your organs and help keep your body warm. Fats help your body absorb some nutrients and produce important hormones, too.
give shape to our body
maintain body temperature in our body
regulate blood pressure and clotting
Excess or Deficiency
High LDL cholesterol increases your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Weight gain. Many high-fat foods such as pizza, baked goods, and fried foods have a lot of saturated fat. Eating too much fat can add extra calories to your diet and cause you to gain weight
Examples
Avocados, Cheese and Dark Chocolate
chips, cookies, butter
3. Proteins
Function
Protein has many roles in your body.
It helps repair and build your body’s tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions.
In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
provide energy, build cell walls and tissue, build structure
Excess or Deficiency
Excess protein consumed is usually stored as fat, while the surplus of amino acids is excreted. This can lead to weight gain over time, especially if you consume too many calories while trying to increase your protein intake.
Too little protein may cause changes in body composition that develop over a long period of time, such as muscle wasting.
The most severe form of protein deficiency is known as kwashiorkor. It most often occurs in children in developing countries where famine and imbalanced diets are common.
Examples
seafood, Skim or low-fat milk, Fat-free or low-fat cheese
Meat, milk, eggs, fish
6. water
Function
Your body uses water in all its cells, organs, and tissues to help regulate temperature and maintain other bodily functions. Because your body loses water through breathing, sweating, and digestion, it's important to rehydrate by drinking fluids and eating foods that contain water
hydration
Excess or Deficiency
People can develop overhydration if they have a disorder that decreases the body’s ability to excrete water or increases the body's tendency to retain water.
Drinking too much water rarely causes overhydration because normal kidneys easily excrete excess water.
Often, no symptoms occur, but in severe overhydration,
people may become confused or have seizures.
Vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, burns, kidney failure, and use of diuretics may cause dehydration.
People feel thirsty, and as dehydration worsens, they may sweat less and excrete less urine.
If dehydration is severe, people may be confused or feel light-headed.
Example
Cucumber, Tomatoes, Spinach
5. Minerals
Function
Minerals are important for your body to stay healthy. Your body uses minerals for many different jobs, including keeping your bones, muscles, heart, and brain working properly. Minerals are also important for making enzymes and hormones.
Excess or Deficiency
But routinely getting an overload of vitamins and minerals can hurt you.
Too much vitamin C or zinc could cause nausea, diarrhea, and stomach cramps. Too much selenium could lead to hair loss, gastrointestinal upset, fatigue, and mild nerve damage.
An increased need for the mineral, lack of the mineral in the diet, or difficulty absorbing the mineral from food are some of the more common reasons.
Mineral deficiencies can lead to a variety of health problems, such as weak bones, fatigue, or a decreased immune system
Examples
meat, cereals, fish
4. vitamins
Function
Vitamins and minerals are considered essential nutrients—because acting in concert, they perform hundreds of roles in the body. They help shore up bones, heal wounds, and bolster your immune system. They also convert food into energy, and repair cellular damage.
bone structure, blood and glucose levels,
Excess or Deficiency
Iron- Nausea, bloody stools, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, fluid build-up in the lungs and fever.
Vitamin A-Hair loss, liver damage, severe headaches, bone pain, blurred vision, dry skin and vomiting
Brittle hair and nails
Mouth ulcers or cracks in the corners of the mouth
Bleeding gums
Poor night vision and white growths on the eyes
Scaly patches and dandruff
Hair loss
Red or white bumps on the skin
Restless leg syndrome
Examples
meat, poultry, fish, and beans
provide calcium,sulfer, iron, zinz,copper