Anatomy
Systems and functions
Nervous System
It controls voluntary actions (conscious movement) and involuntary actions (unconscious movement such as breathing), and sends signals to different parts of the body.
Nervous System
Central Nervous System

Brain

Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nervous System
It is formed by the nerves that connect each part of the body with the central nervous system.

Digestive system
It is made up of a series of connected organs, which allow food to be broken down and absorbed, and waste to be disposed of.
Includes
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus.
The liver and pancreas also play an important role in the digestive system as they produce juices that help break down food, bile and pancreatic juice.
The first sign of digestive tract problems often includes one or more of the following symptoms:
Diarrhea
Constipation
Incontinence
Nausea and vomiting
Stomach pain
Swallowing problems
Muscular System
It is made up of 650 muscles that aid in movement, blood flow and other bodily functions.
There are three types of muscle
Skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
Urinary System
The urinary system helps eliminate urine, the waste product formed in the body.
It is made up of:
.
Circulatory System
Circulatory system is responsible for moving blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones around the body.
composed of

Blood
Blood it's a type of fluid connective tissue.
composed of
Glóbulos Blancos
Plaquetas
Plasma
Glóbulos Rojos
Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and eliminates waste.

Blood vessels
Arteries
Veins
Heart
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.

Respiratory System
Respiratory system allows oxygen to be obtained from the outside for incorporation into the cells and to expel the carbon dioxide produced as a result of cellular activity.
composed of
Conducting Zone
The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air.
Composed of
Nose
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchioles

Lungs
They are two sponge-like organs in the form of a sac.
They are composed of
Bronchioles
Pulmonary alveolus
They are protected by
The rib cage
Ribs
Sternun
A membrane that surrounds them called Pleura
They contract and dilate thanks
to their elastic properties.
to the movement of the muscles located between the ribs and the diaphragm.
Gas exchange takes place in them.
Diseases affecting the respiratory system.

The flu
It's a contagious respiratory disease caused by the influenza virus.
some symptoms may include
Fever
Cough
Sore throat
Nasal discharge or congestion
Muscular or body pains
Headaches
fatigue (tiredness)

Skin
Skin is the body's largest organ. It protects us from external factors, and is our first defense against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens.
helps us to
Regulating our body temperature and eliminating waste through perspiration
Body parts involved:
Upper extremities
for example
neck, shoulders, chest, arms, back, fingers.
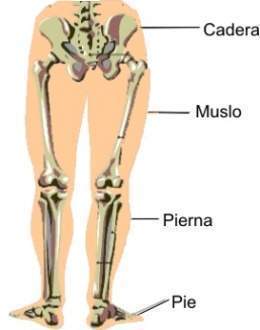
Lower extremities
for example
hips, thighs, legs, knees, feet.
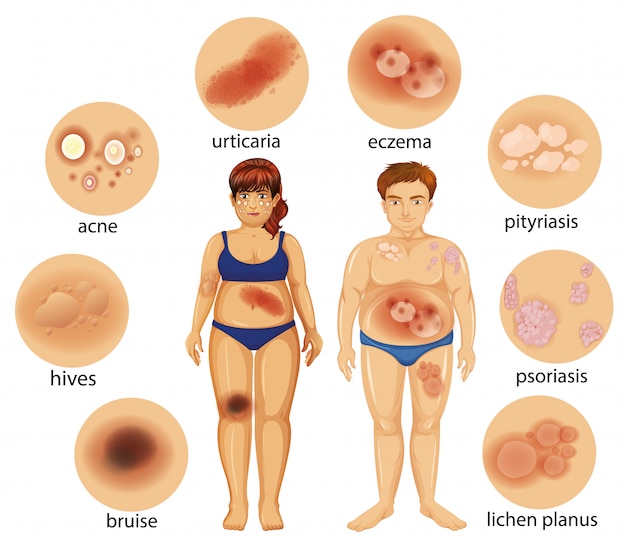
Some skin Irregularities that are usually symptoms of a skin disorder include
Scaly skin
Raised red or white protuberances
A rash, which may be painful or itchy
Changes in the color or size of a mole
Excessive redness
Members:
Nicole Romero
Hazar Yufla