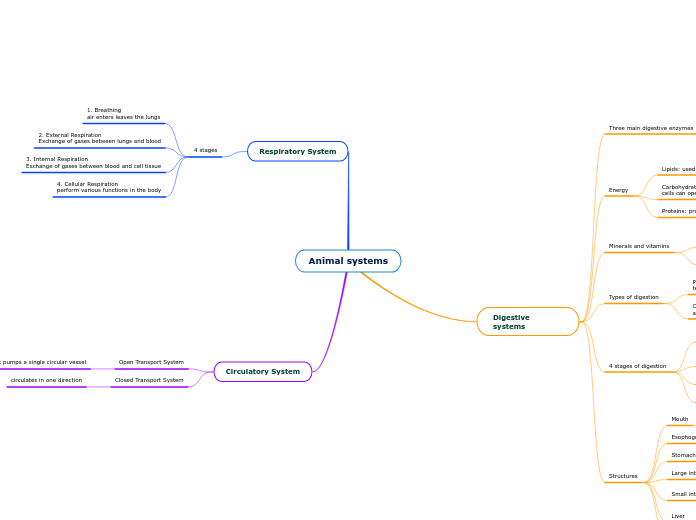
Animal systems
Digestive systems
Three main digestive enzymes
Amylase: breaks starch into glucose
Protease: breaks protein into amino acids
Lipase: fat breaks into fatty acids and glycerol
Energy
Lipids: used for storing energy,
Carbohydrates: needed by all body cells as energy so nerve cells can operate
Proteins: provide structure and support
Minerals and vitamins
Vitamins: Does not obtain energy but can assist with energy related processes
Minerals: bodies need to develop and function normally
Types of digestion
Physical/Mechanicalbreaks down food into smaller pieces using teeth
Chemical: enzymes and water break down food so it is absorbed
4 stages of digestion
ingestion: Taking the nutrients
Digestion: breakdown of complex organic molecules into smaller components by enzymes
Absorption: transport of digested nutrients to tissues
Elimination: removal of waste food materials
Structures
Mouth
breaks down food and lubricates it
Esophogus
where food travels
Stomach
food storage
Large intestine
stores wastes so minerals and vitamins can be absorbed
Small intestine
breakdown and absorption of remaining proteins and carbohydrates
Liver
detoxifying blood
Gallbladder
stores bile
Respiratory System
4 stages
1. Breathing
air enters leaves the lungs
2. External Respiration
Exchange of gases between lungs and blood
3. Internal Respiration
Exchange of gases between blood and cell tissue
4. Cellular Respiration
perform various functions in the body
Circulatory System
Open Transport System
insets heart pumps a single circular vessel
Closed Transport System
circulates in one direction