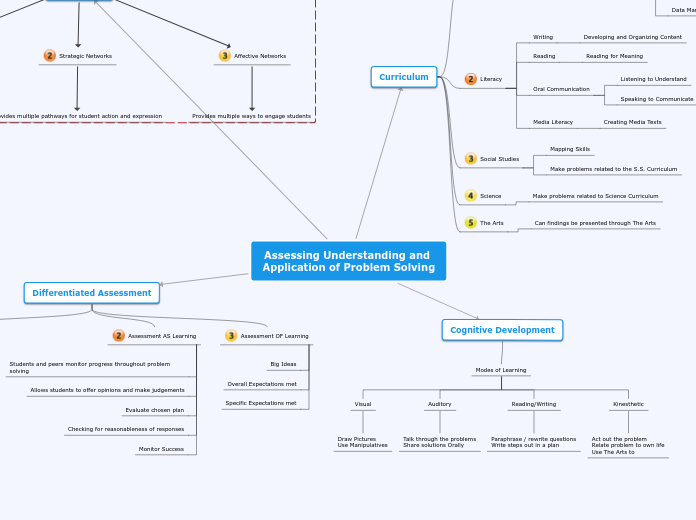
Assessing Understanding and Application of Problem Solving
Universal Design
Recognition Networks
Uses multiple ways to present information
Strategic Networks
Provides multiple pathways for student action and expression
Affective Networks
Provides multiple ways to engage students
Differentiated Assessment
Assessment FOR Learning
Selection of Problem-solving strategies
Communication
Assessment AS Learning
Students and peers monitor progress throughout problem solving
Allows students to offer opinions and make judgements
Evaluate chosen plan
Checking for reasonableness of responses
Monitor Success
Assessment OF Learning
Big Ideas
Overall Expectations met
Specific Expectations met
Curriculum
Mathematics - Problem Solving is one of the Processes
Number Sense and Numeration
Measurement
Geometry and Spatial Sense
Patterning and Algebra
Data Management and Probability
Literacy
Writing
Developing and Organizing Content
Reading
Reading for Meaning
Oral Communication
Listening to Understand
Speaking to Communicate
Media Literacy
Creating Media Texts
Social Studies
Mapping Skills
Make problems related to the S.S. Curriculum
Science
Make problems related to Science Curriculum
The Arts
Can findings be presented through The Arts
Cognitive Development
Modes of Learning
Visual
Draw Pictures
Use Manipulatives
Auditory
Talk through the problems
Share solutions Orally
Reading/Writing
Paraphrase / rewrite questions
Write steps out in a plan
Kinesthetic
Act out the problem
Relate problem to own life
Use The Arts to