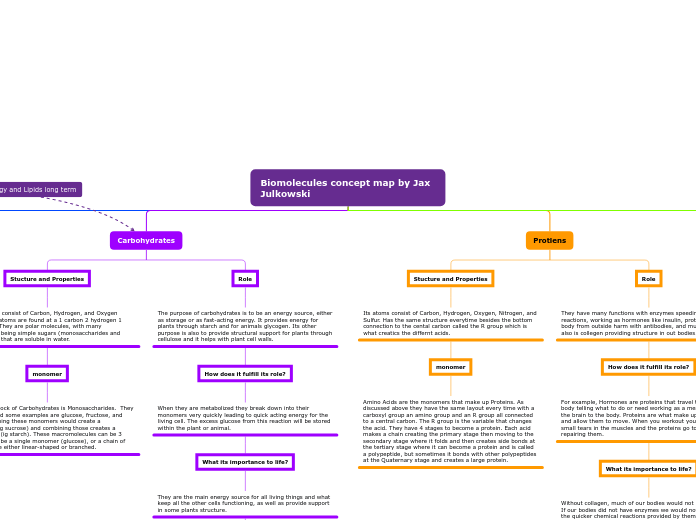
Biomolecules concept map by Jax Julkowski
Lipids
Stucture and Properties
They are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen atoms. Almost all Lipids are Non-polar and Hydrophobic.
monomer
They are made up of triglyceride monomers. Triglycerides consist of Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids. They can be Saturated or Unsaturated fats with the difference being that Unsaturated fats carbon skeleton contains double bonded carbons. An important polymer of lipids are phospholipids that have a polar end and a nonpolar end that serve as cell membrane walls with one end being hydrophobic and the other being hydrophillic so it can interact with water and other cells.
Role
They are used as long term energy storage in living things and also serve as cell membrane walls (phospholipids).
How does it fulfill its role?
Compared to carbohydrates which also have to do with energy and release it all at once quickly lipids slowly release their energy. Phospholipids work as cell membrane walls since they work like a sandwich, in which both the nonpolar ends face towards the middle and the polar ends face the outside so that the wall can interact with water and the middle stops anything from getting in.
What its importance to life?
Without them cells would not be able to form. Also the long term energy source is needed for livings things survival since cells need a consist flow of energy that carbohydrates cannot provide.
Real life examples
Some example are fats, oils, and waxes. The fat on your stomach is made from lipids when you eat to much and you body stores the excess energy in form of lipid as long term storage. Also all our cells have them for membranes.
Carbohydrates
Stucture and Properties
Carbohydrates consist of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen atoms. These atoms are found at a 1 carbon 2 hydrogen 1 Oxygen ratio. They are polar molecules, with many carbohydrates being simple sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides) that are soluble in water.
monomer
The building block of Carbohydrates is Monosaccharides. They are 1 sugar and some examples are glucose, fructose, and ribose. Combining these monomers would create a disaccharide (ig sucrose) and combining those creates a polysaccharide(ig starch). These macromolecules can be 3 shapes: it can be a single monomer (glucose), or a chain of sugars that are either linear-shaped or branched.
Role
The purpose of carbohydrates is to be an energy source, either as storage or as fast-acting energy. It provides energy for plants through starch and for animals glycogen. Its other purpose is also to provide structural support for plants through cellulose and it helps with plant cell walls.
How does it fulfill its role?
When they are metabolized they break down into their monomers very quickly leading to quick acting energy for the living cell. The excess glucose from this reaction will be stored within the plant or animal.
What its importance to life?
They are the main energy source for all living things and what keep all the other cells functioning, as well as provide support in some plants structure.
Real life examples
Foods like bread and noodles and certain fruits are carb heavy. Before big games when athletes need quick burst of energy they will have carb heavy meals to gain that energy boost.
Protiens
Stucture and Properties
Its atoms consist of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur. Has the same structure everytime besides the bottom connection to the cental carbon called the R group which is what creatics the differnt acids.
monomer
Amino Acids are the monomers that make up Proteins. As discussed above they have the same layout every time with a carboxyl group an amino group and an R group all connected to a central carbon. The R group is the variable that changes the acid. They have 4 stages to become a protein. Each acid makes a chain creating the primary stage then moving to the secondary stage where it folds and then creates side bonds at the tertiary stage where it can become a protein and is called a polypeptide, but sometimes it bonds with other polypeptides at the Quaternary stage and creates a large protein.
Role
They have many functions with enzymes speeding up chemical reactions, working as hormones like insulin, protecting the body from outside harm with antibodies, and much more. It also is collegen providing structure in out bodies.
How does it fulfill its role?
For example, Hormones are proteins that travel through the body telling what to do or need working as a messenger from the brain to the body. Proteins are what make up our muscles and allow them to move. When you workout your body makes small tears in the muscles and the proteins go to work repairing them.
What its importance to life?
Without collagen, much of our bodies would not hold together. If our bodies did not have enzymes we would not survive as the quicker chemical reactions provided by them are essential to our lives. We would all die very quickly if we did not have antibodies since we would always be getting sick with no way to react to it.
Real life examples
After eating and glucose is poured into our bloodstream insulin is sent in to manage our blood sugar. When we get sick antibodies fight against the virus so that it can slow and stop the spread between cells.
Nucleic Acids
Stucture and Properties
They are made up of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and phosphate. They are polar molecules that are water soluble.
monomer
Nucleotides are the base of Nucleic acids. Each Nucleotide contains a 5-carbon sugar either deoxyribose(DNA) or ribose (RNA) a phosphate group and a Nitrogen base. The nitrogen base is what differs for each Nucleotide and what makes them unique. The base can either be Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine (DNA), or Uracil (RNA). When nucleotides connect they must be between certain nitrogen bases A and T/U combined and G and C combine with G and C connection being stronger since they have 3 hydrogen bonds compared to 2.
Role
It stores inherited cellular data (DNA) and carries the information around (RNA).
How does it fulfill its role?
To differ data the mix up of A and T/U connection with G and C connection are what make each unique DNA molecule different and the RNA's job is to carry the DNA information around.
What its importance to life?
Without it there would be no DNA or RNA and no genetic information meaning everything would either not exist or all be the same.
Real life examples
Every person is unique in all aspects and there DNA is unique and that is why you can pinpoint a criminal though DNA investigation.