British North America Act
Enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in 1876Union of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick, and the Government thereofSets the framework for the operation of the Government of Canada and defines the following:Federal StructureHouse of Commons of CanadaThe SenateThe Justice SystemThe Taxation System
Canadian Constitution / Charter of Rights
It is the supreme law in CanadaOutlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in CanadaSets out those rights and freedoms that Canadians believe are necessary in a free and democratic society
Treaties with Indigenous Peoples
Provide a framework for living together and sharing the land Indigenous peoples traditionally occupiedIncluded the following treaties:Treaties of Peace and Neutrality (1701-1760)Brought an end to more than 150 years of relations and alliances between France and the Aboriginal people of the St. Lawrence ValleyPeace and Friendship Treaties (1725-1779)Regularised trade and assure a stable peaceUpper Canada Land Surrenders and the Williams Treaties (1764-1862/1923)The agreements surrendered Indigenous lands to the colonial government for a variety of purposes, including settlement and development
Canadian Democracy
The Crown and Constitutional Monarchy
Abstract concept or symbol that represents the state and its governmentNon-partisan sovereign authority. It is part of the legislative, executive and judicial powers that govern the countryConstitutional monarch, in contrast, is limited by the laws of the ConstitutionDo not directly rule; carry out constitutional, ceremonial and representational dutiesCurrently Charles III is the head of the monarch
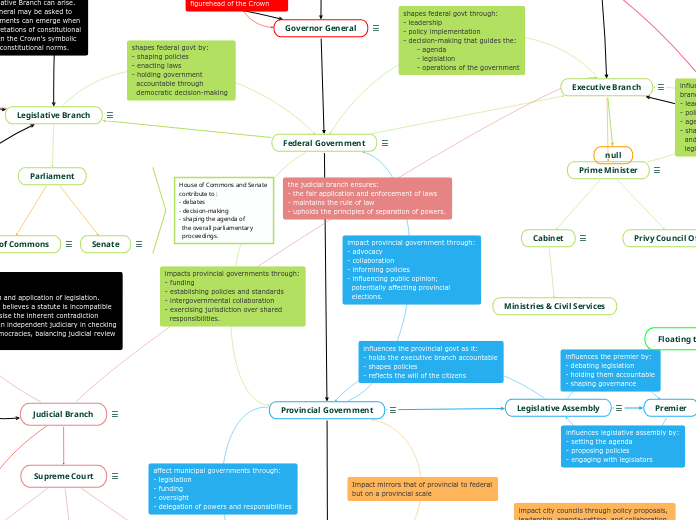
Governor General
Duties are carried out by the governor general, who acts as the representative of the Crown — currently Mary Simon — in CanadaFigurehead of the Crown and Constitutional MonarchyUphold the traditions of Parliament and other democratic institutionsCeremonial position and holds no democratic power
Federal Government
Responsible for areas of national interest such as immigration, defence and trade with other countriesThe term can refer narrowly to the Canadian Cabinet, or more broadly to the Cabinet and the public serviceThe type of government is above the Provincial and Municipal government
Provincial Government
The provincial government is responsible for issues that affect the province as a wholeIncludes education, health care, the environment, agriculture and highwaysIs placed above the Municipal government
Municipal Government
Responsible for providing many of the services within their local boundaries that you rely on daily,Includes strategic land use, subdivision and condominium approval, and maintenance of the local roads, including snow removalIs the lowest form of government; placed below the provincial government
Citizens
Citizens Groups
(advocacy/lobby groups)
Play a crucial role in amplifying the voices of individuals who share common interests or concernsThese groups can have a significant influence on the development and implementation of policiesAdvocacy and lobby groups act as watchdogs, holding governments, corporations, and other powerful entities accountable for their actionsBy highlighting issues and seeking transparency and accountability, citizens groups contribute to a more accountable and responsive society
Free and Independent Press
Provides accurate and timely information to the publicInvestigates and reports on events, issues, and policies, enabling citizens to make informed decisions and participate in democratic processesScrutinizes the actions of government officials, institutions, and other powerful entitiesServes as a platform for diverse voices, allowing for open debates and discussions on various social, political, and economic matters
Free and Fair Elections
Play a crucial role in ensuring that citizens have the opportunity to choose their representatives and leadersFoster accountability among elected officialsThe possibility of being voted out of office encourages responsible governance
City Council
Responsible for creating, amending, and repealing local laws and ordinances that govern the cityThey establish priorities, set goals, and develop strategic plans to address the needs and interests of the communityCity councils act as representatives of the community they serve
Mayor
Serves as the chief executive officer of the cityProvide leadership and direction to the city's administration and oversee the implementation of policies and programsAct as the official spokesperson for the city and often serve as a liaison with other levels of government, community organizations, and business entitiesWork with city staff and the city council to develop the annual budget, allocate resources, and prioritize spendingCurrently, the Mayor of Brampton is Patrick Brown
Legislative Assembly
The primary role of the Legislative Assembly is to make lawsElected representatives, also known as Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs) or Members of Parliament (MPs), propose, debate, and vote on legislationRepresents the interests and concerns of the constituents it serves; MPs act as the voice of the people, advocating for their constituents' needs, aspirations, and concernsExercises oversight and scrutiny over the executive branch of governmentReview and scrutinize the proposed budget, debate its allocations, and vote on its approval
Premier
Serves as the head of the provincial or state governmentResponsible for leading the executive branch and overseeing the administration of the province/stateWork with government ministers and departments to formulate policies, set priorities, and establish the direction for the province/stateAct as the chief spokesperson for the government, communicating government policies, initiatives, and decisions to the publicResponsible for making critical decisions, managing resources, and ensuring public safety and well-beingThe current premier of Ontario is Doug Ford
Legislative Branch
Responsible for making lawsConsists of elected representatives who propose, debate, and vote on legislationElected representatives act as the voice of the citizens they represent, advocating for their needs, opinions, and valuesServes as a counterweight to the executive branch, ensuring that the government's powers are not concentrated in one authorityReviews and approves the government's budget proposals, ensuring that public funds are allocated appropriately and in accordance with the priorities of the country
Parliament
House of Commons
One of the two houses of the Parliament of Canada and is responsible for making laws at the federal levelMembers of Parliament (MPs) in the House of Commons propose, debate, and vote on legislation; represent their constituents and contribute to the development and passage of laws that impact the entire countryElected by the public through general elections and act as the voice of their constituentsPlays a vital role in government formation and accountability
Senate
Has the role of reviewing and scrutinizing legislation proposed by the House of CommonsSenators carefully examine bills, offer amendments, and provide a second look at proposed laws to ensure their quality, effectiveness, and adherence to constitutional principlesAppointed to represent specific regions or provinces, bringing their regional expertise and perspectives to parliamentary discussionsThe Senate acts as a "sober second thought" on legislation, providing an independent and objective evaluation of proposed lawsConducts studies, inquiries, and investigations on various matters of public policy
Executive Branch
Responsible for the administration and governance of a country or jurisdictionResponsible for implementing and enforcing laws and policies enacted by the legislative branchInvolves various government agencies, departments, and ministries responsible for specific areas of governanceRepresents the country in international relations, negotiates treaties and agreements, maintains diplomatic relationships with other nations, and participates in international organizationsHeaded by PM
Prime Minister
Serves as the head of the executive branch of the Canadian government; provides overall leadership and direction to the government and its various departments and agenciesWork with cabinet members and advisors to develop policy proposals, set priorities, and make decisions on various issues affecting the countryAppoints and manages the cabinetRepresents Canada domestically and internationally; serve as the chief spokesperson for the government, communicating its policies, initiatives, and decisions to the public
Cabinet
A group of senior government ministers selected by the Prime MinisterThe primary role is to assist the Prime Minister in developing and implementing government policiesProvide leadership, set departmental priorities, and ensure the effective administration of government programs and servicesOperates on the principle of collective responsibility, which means that all cabinet members are collectively accountable for government decisions and actionsServe as representatives of the government and liaise with various stakeholders, including interest groups, businesses, and the public
Ministries & Civil Services
Privy Council Office
Serves as the central agency that provides non-partisan advice and support to the Prime MinisterAssists the Prime Minister in policy development, decision-making, and coordination of government activitiesSupports the functioning of the Cabinet by coordinating cabinet meetings, preparing agendas, and providing administrative supportAlso supports the implementation of government priorities and initiatives across various departments and agencies, promoting efficiency and effective delivery of servicesFosters interdepartmental coordination and collaboration, facilitating communication and cooperation among different government departments and agencies
null
House of Commons and Senate
contribute to :
- debates
- decision-making
- shaping the agenda of
the overall parliamentary
proceedings.
Both Cabinet and Privy Council provide:
- policy advice
- expertise, and support
- contribute to decision-making
- shape the priorities and direction of the
PM's leadership.
Judicial Branch
Responsible for interpreting and applying laws to resolve legal disputesPlays a critical role in upholding the Constitution and protecting individual rights and libertiesProvides a forum for individuals and organizations to resolve disputes and seek justice
Supreme Court
The Supreme Court serves as the highest judicial authorityActs as the final arbiter of the law, ensuring uniformity and consistency in the interpretation and application of legal principlesHas the authority to review and overturn decisions made by lower courts.Supreme Court decisions establish legal precedents that guide future rulings.
Federal Court
It hears cases involving federal legislation, regulations, and disputes involving the federal governmentPlays a crucial role in judicial review; reviews decisions made by federal administrative bodies and agencies to ensure they are lawful, reasonable, and compliant with federal laws and regulationsActs as a forum for resolving disputes involving the federal government as a party
Provincial Court
Handles a wide range of cases related to provincial laws and regulationsProvides a forum for individuals and organizations to resolve legal disputes within the jurisdiction of the specific provinceAlso handles initial court appearances, bail hearings, and preliminary matters in criminal cases
Tax Court
The primary role of the Tax Court is to resolve disputes between taxpayers and tax authorities regarding the interpretation and application of tax lawsReviews cases related to various tax matters, including income tax, corporate tax, sales tax, and other tax-related issuesProvides an independent and impartial venue for taxpayers to resolve disputes, promoting transparency and accountability in the tax system