Chapter 9: Leading
By Sajeevan

Nature of Leadership

Leadership:
Inspiring others to work hard

Leadership and Vision

Servant Leadership

Commitment to serving others

Followers more important than leader
Other-centered not self-centered

Focuses on empowerment, not on power
Empowerment meaning: managers enable and help others to gain power and achieve influence.

Instead of the people working to serve the leader, the leader exists to serve the people
Effective leaders empower others by providing

Information

Responsibility

Authority

Trust

Leadership and Power:

Power:
ability to get someone to do something
Two sources of managerial power:

Position power
the manager’s official status in the organization’s
Sources of position power:

Reward power: Capable of offering something of value

Coercive power: Capable of delivering punishment or
withhold positive outcomes

Legitimate power: Organizational position or status
confers the right to control those in subordinate positions

Personal power
Meaning: unique personal qualities that a person brings
Sources of personal power:

Expert power: is the perception that a certain person has an elevated level of knowledge or a specific skill set that others in an organization don't have

Referent power: Capacity to influence other people
because they admire you and want to identify positively
with you

Relational power: the ability to work and function well as
part of a team working toward a collective goal

Contemporary leadership challenges:

1. Shorter time frames for accomplishing things

2. Expectations for success on the first attempt

3. Complex, ambiguous, and multidimensional problems

4. Taking a long-term view while meeting short-term demands

Leadership Traits and Behaviours

Leadership Traits

Drive
Self-confidence

Creativity
Cognitive ability
/iStock-637972224-59ee2fc7c412440011686a40.jpg)
Job-relevant knowledge
Motivation
Flexibility

Honesty and integrity

Leadership Behaviours
Theories focus on how leaders behave
when working with followers
Basic dimensions of leadership behaviors:
Concern for the task to be accomplished

Plans and defines work to be
done
Assigns task responsibilities

Sets clear work standards
Urges task completion

Monitors performance results
Concern for the people doing the work

Acts warm and supportive
toward followers
Develops social rapport with
followers

Respects the feelings of
followers
Is sensitive to followers’ needs

Shows trust in followers

Classical Leadership Styles
Recurring patterns of behaviours
exhibited by a leader.

Autocratic style:
where one person controls all the decisions and takes very little inputs from other group members

Laissez-faire style:
where let their employees use their creativity, resources, and experience to help them meet their goals

Democratic style:
where members of the group take a more participative role in the decision-making process, and
helping people develop skills and competencies
Communication

Communication:
An interpersonal process of sending and receiving symbols with messages attached to them
Key elements of the communication process

Sender
Message

Communication channel
Receiver
Interpreted meaning

Feedback

Communication Barriers
Poor choice of channels:

A communication channel is the pathway or medium through which a message moves from sender to receiver.
Written channels work for messages that

Are simple and easy to convey
Require extensive dissemination quickly

Convey formal policy or authoritative directives
Spoken channels work for messages that
Are complex or difficult to convey where immediate feedback is needed

Attempt to create a supportive, even inspirational, climate
Poor written or oral expression: How to make it successful?

Be prepared
Set the right tone
Sequence points
Support your points
Accent the presentation
Add the right amount of polish

Check your technology

Don’t bet on the internet

Be professional
Failure to recognize nonverbal signals:

Nonverbal communication takes place
through gestures, facial expressions,
body postures, eye contact, and use of
interpersonal space

Mixed messages occur when a person’s
words and nonverbal signals
communicate different things

The growing use of communication
technologies causes important
nonverbal communication to be lost

Physical Distraction:

Include interruptions from telephone calls, drop-in visitors, a lack of privacy, etc.
Can interfere with the effectiveness of a communication attempt

Can be avoided or at least minimized through proper planning
Subtopic

Status effects:
Occur when an organization’s hierarchy of authority creates a barrier to effective communication
Status effects include:
Filtering: the intentional distortion of information to make it
appear favourable to the recipient
Employees acing as “yes men”

Improving Communication

Active Listening
The process of taking action to help someone say exactly what they really means.
Rules for active listening:

Listen for message content
Listen for feelings

Response to feelings
Note all cues, verbal and nonverbal
Paraphrase and restate

Constructive Feedback
Feedback is the process of telling someone else how you feel about something that person did or said.
Constructive feedback guidelines:

Give it directly

Make it specific
Give it when the receiver is willing or able to accept it

Make sure it is valid
Give it in small doses
Space Design:

The range between people
carries varying purposes in
terms of intimacy, openness,
and state in interpersonal
communications.
Interpersonal space is an
important nonverbal cue.

Communication Channels Selection
Managers need to choose a channel with the appropriate richness for the communication.
Channel richness is the capacity of a communication channel to carry information in an effective manner.
Low channel richness is impersonal, one-way, and fast
High channel richness is personal, two-way, and slow

Electronic Communication
Read items once

Take action immediately
Purge folders of useless messages
Send short messages in the subject line

Send group mail and reply to all only when necessary
Get off distribution lists

Put large files on websites
Use instant messaging as an alternative

Don’t forget email privacy

Interactive Management

MBVA (Management by Wandering Around)
Managers spend time outside their offices to meet and talk with workers at all levels.
Refers to a style of business management which involves managers wandering around, in an unstructured manner, through the workplace, at random, to check with employees, equipment, or on the status of ongoing work.

Electronic Forms
Online discussion forums, chat rooms, electronic office hours,
executive blogs, and video conference, etc.

Cross-Cultural Communication
Non-verbal communication:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/illo_BodyLanguage-Eyes2-5984a36868e1a20011080f97.gif)
Eye movements
Touching

Body motions

Language
Ethnocentrism

The tendency to consider one’s culture superior to any and all others
Not listening to others

Inappropriate stereotypes
Issues in Leadership Development

Super leaders
Persons whose vision and strength of personality have an extraordinary impact on others

Charismatic leaders
Develop special leader-follower relationships and inspire others in extraordinary ways

Transformational leadership
Someone who is truly inspirational as a leader and who arouses others to seek extraordinary performance accomplishments
Characteristics of transformational leaders:

Vision
Charisma

Symbolism
Empowerment

Intellectual stimulation

Integrity

Transactional leadership
Someone who directs the efforts of others through tasks, rewards, and structures
Characteristics of transactional leadership:

Revel inefficiency
Tend to be inflexible

Opposed to change

Favour structured policies and procedures

Thrive on following rules and doing things correctly
Very left-brained

Emotional Intelligence and Leadership
The ability of people to manage themselves and their relationships effectively
Components of emotional intelligence:

Self-awareness
Self-regulation

Motivation
Empathy

Social skill
To be effective, leaders must have a solid understanding of how their emotions and actions affect the people around them

Gender and Leadership
Both women and men can be effective leaders.

Women tend to use interactive leadership.

Leaders who are strong communicators and act in a democratic and participative manner with followers.

Provide a good fit with the demands of a diverse workforce and the new workplace.
Men tend to use transactional leadership.

Someone who values order and structure

Depends on self-motivated people who work well in a structured, directed environment
Future leadership success will depend
on a person’s capacity to

Openness
Positive relationships
Empowerment

Support

Moral Leadership
Moral leadership is always “good” and “right” by ethical standards.

High ethical standards of behaviour

Build and maintain an ethical organizational cultural

Both help and require others to behave ethically in their work

A leader with integrity is honest, credible, and consistent in putting values into actions.
Authentic Leadership activates positive psychological states to achieve self-awareness and positive self-regulation.

Confident, hope, optimism, and resilience.
Authentic leaders clearly frame moral dilemmas, transparently respond to them, and consistently serve as ethical role models.
“A leader's behavior that demonstrates superior virtues, self-discipline, and unselfishness”

Drucker’s “Old-Fashioned” Leadership
Essentials of “old-fashioned” leadership:

Defining and establishing a sense of mission

Accepting leadership as a “responsibility” rather than a rank or class

Earning and keeping the trust of others

Hard working makes a successful leader.

Drucker strongly believed things such as "leadership qualities" or a "leadership personality" were given more emphasis than they should be
Contingency Approaches to Leadership

Fiedler’s Contingency Model

Good leadership depends on a match between leadership style and situational demands
To determine a person’s leadership style the least-preferred co-worker scale is used

Leadership is part of one’s personality, and therefore relatively enduring and difficult to change
Leadership style must be fit to the situation
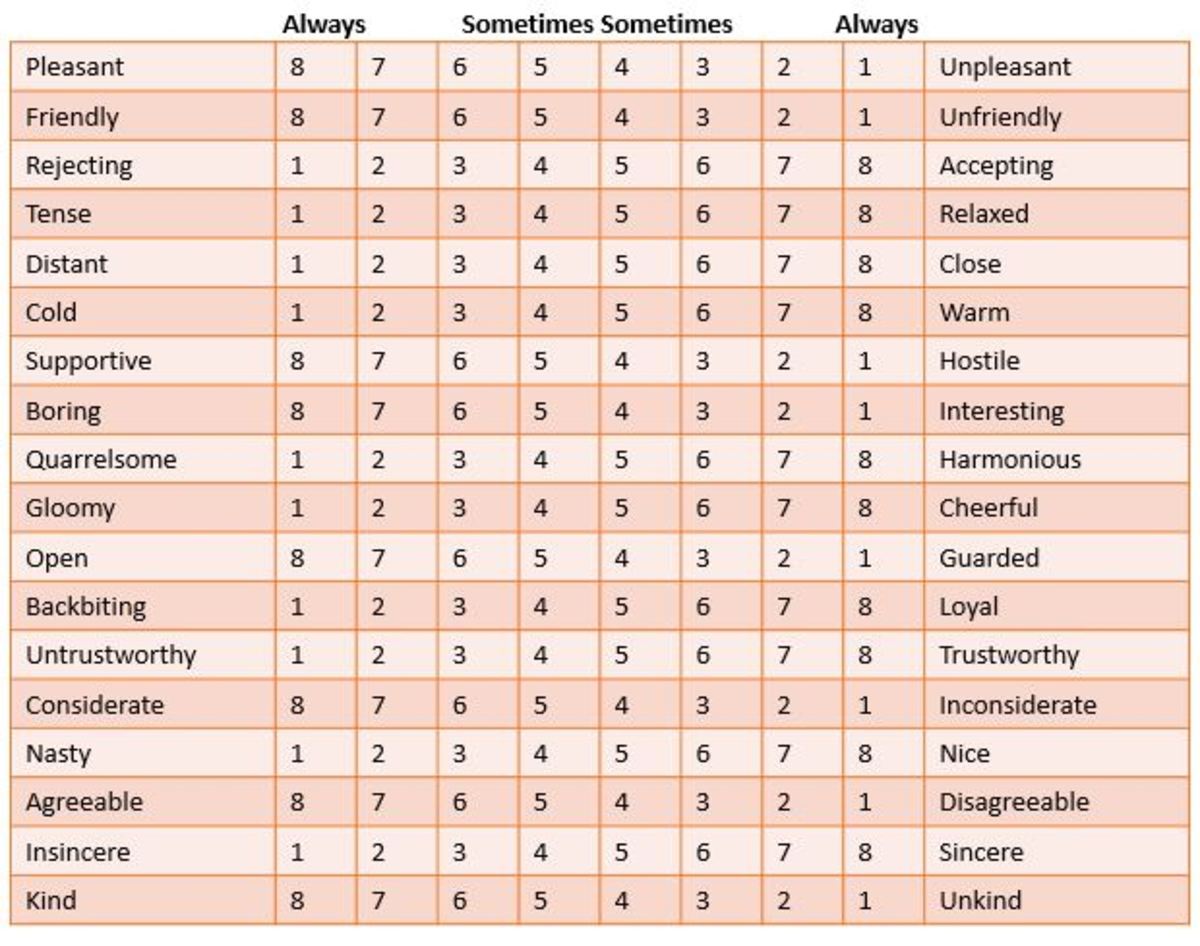
LPC scale asks a person to think of someone they have difficulty with to get a job done
What is LPC score?

Low LPC: task-motivated leaders
High LPC: relationship-motivated leaders
"Least-preferred coworker" scale, developed by American scholar Fred Fiedler, identifies whether an individual's leadership style is either relationship-leaders or task-leaders
Fiedler's contingency model is a dynamic model where the personal characteristics and motivation of the leader are said to interact with the current situation that the group faces

Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model
Leaders adjust their styles depending on the readiness of their followers
to perform in a given situation. Readiness: how able and willing or confident followers are to perform
required tasks.

Participating
Low-task, low-relationship style
Works best in high readiness situations

Delegating
Low-task, high-relationship style
Works best in low to moderate readiness situations

Selling
high-task, high-relationship style
Works best in moderate to high readiness situations

Telling
high-task, low-relationship style
Works best in low readiness situations
Hersey-Blanchard Model suggests no single leadership style is better than another. Instead of focusing on workplace factors, the model suggests leaders adjust their styles to those they lead and their abilities

House’s Path-Goal Leadership Theory
Directive leadership

Communicate expectations
Give directions

Schedule work
Maintain performance standards
Clarify leader’s role

When Job assignments are unclear
Supportive Leadership

Treat group members as equals
Be friendly and approachable

Show concern for employee's well-being

When Workers self-confidence is low

An effective leader clarifies paths by which followers can achieve goals. An employee's perception of expectancies between his effort and performance is greatly affected by a leader's behaviour
Achievement-Oriented Leadership

Set unique goals
Expect high performance levels

Emphasize continuous improvement
Display confidence in meeting high standards

When Task challenging is insufficient
Participative Leadership

Involve subordinates in decision making
Consult with subordinates

Ask for suggestions from toehrs
Use suggestions

When Performance incentives are poor

Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory
Not all people are treated the same by leaders in leadership situations
In groups: high LMX

Getting rewards, increase in promotion

Access to information

Other favourable treatments than others
Out groups: low LMX

Fewer rewards

Less information causes more difficulty

Little or no special attention, lack of communication

Vroom-Jago Leader Participation Model

Helps leaders choose the method of decision making that best fits the nature of the problem situation

Basic decision-making choices:
Authority decision
Consultative decision
Group decision

Authority decision
Only leader decides and then communicated to the group
Works best when

Leader has greater expertise

Confident and capable

Acceptance from others

Little or no time

Consultative Decision
Leader only decides after seeking advice, opinions from group
members
Work best when

Leader lacks sufficient expertise and information

Problem is unclear

Need acceptance from others to work

Time available

Group Decision
Decision is made by group members themselves