Circular Motion
Angular Velocity
Formulas

Meaning
"Angular velocity" is a measure of turning per time unit. It tells you the size of the angle through which something revolves in a given timespan
Banked Curves
Meaning
A banked turn (or banking turn) is a turn or change of direction in which the vehicle banks or inclines, usually towards the inside of the turn.

Example
A banked surface is one that slopes upward towards the outer edge of a curve. Banked surfaces exist at on-ramps to highways because cars have to start traveling faster to enter the highway.

Centripetal Force
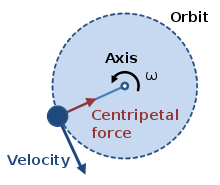
Meaning
The unbalanced force acing on an object in uniform circular motion is called Centripetal force, Fcent
Is a force pushing or pulling the object towards the center of the circle.
Formula
The unbalanced force acing on an object in uniform circular motion is called Centripetal force, Fcent
Is a force pushing or pulling the object towards the center of the circle.
Features
1. Size is constant
2. Direction is towards the centre of the circular path
Example
A motorbike and rider of total mass 100 kg travel round a roundabout of radius 8 m at a speed of 4 m/s.
.
What is the centripetal force needed to do this?
F = mv2/r = [100 x 42]/8 = 200 N.
Formulas
Net Force
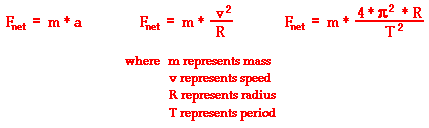
Speed
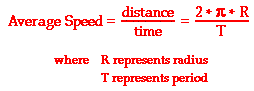
Acceleration

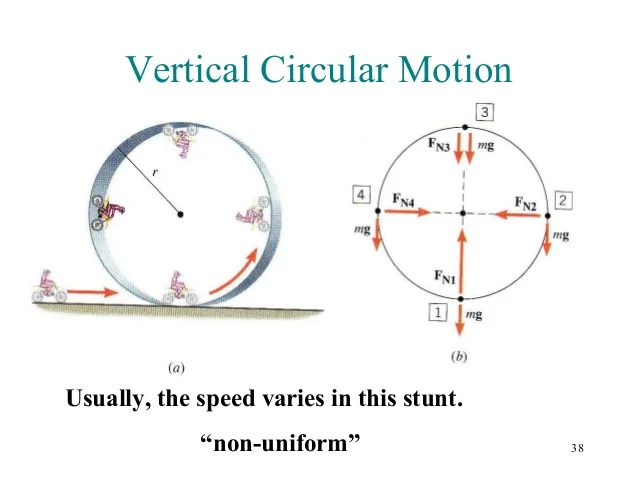
Vertical Circular Motion
Meaning
A body revolves in a vertical circle
such that its motion at different points
is different then the motion of the body
is said to be vertical circular motion.
Examples
Common examples include:
roller coasters

Wheels
Centripetal Acceleration
Features
1. Size is constant
2. Direction is towards the centre of the circular path
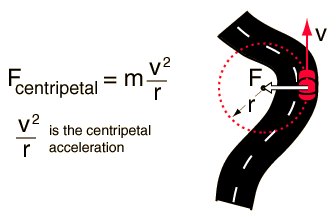
Formula
CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION = v2/r
Meaning
We call the acceleration of an object moving in uniform circular motion—resulting from a net external force—the centripetal acceleration.
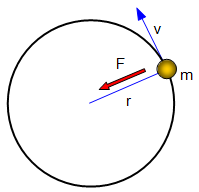
Example
A stone is whirled round on the end of a 1.5 m long piece of string. If the acceleration of the stone is 3g (30 m/s2) calculate the speed at which the stone is moving.
Use: a = v2/r so v2 = ar = 30x1.5 = 45 and so v = [45]1/2 = 6.7 m/s