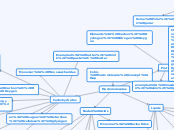
Cohn- Macromolecule Concept Map
Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Monomer: Monosaccharides
Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Functions: quick energy, energy storage, structure of plants
Examples: butter, milk, pasta, butter
Characteristics: structure=function, carbs=sugars, sugars end in -ose (glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose), cellulose is found in the structure of plants, sugars classified by number of carbons


Characteristic: Always in 1:2:1 ratio
Ex: C6H12)6
ex: sugars, starches, cellulose, gllycogen
Lipids
Monomer: Triglycerides
Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Functions: Energy storage, cushion organs, insulates body
Examples: fats, oil, phospholipids, steroids, wax
Characteristics: Lipids are not polar and hydrophobic, saturated v unsaturated fats, phospholipid has hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head, structure: glycerol and 2 fatty acids, comprise most of cells membrane, phospholipids found in the cell membrane
Long hydrocarbon chain
structure: glycerol+ fatty acid


Subtopic
Proteins
Monomer: Amino Acids
Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen Oxygen
Functions: hormones, muscle movement, protect against germs (immune system), transports substances throughout the body
examples: muscle, hair, skin, pepsin
Characteristics: Peptide bonds, 4 layers- structure, chain coils or folds, shape allows proteins to do their job, 20 0f their monomers ( amino acids) found in living organisms, r group and functional group, without shape proteins will dissolve and die, temperature and pH can denature a protein
Amino acid chained to plymer
Eacn amino acid is the same excpet for the variable (function ) gourp.
Some Polar, some non polar
4 layers and their structure:
Primary layer-sequence of amino acids
Secondary layer- chains coil or fold. Two types: alpha helix and pleated sheet
Tertiary layer: attraction between alpha helices and the beta sheets
Quaternary Layer: one or more chains bonded together ex: collagen and hemoglobin


Nucleic Acids
Monomer: Nucleotides
Elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Nitrogen
Functions: make up DNA and RNA store and transfer information from parents to offspring, hereditary information (transmit and store)

Characteristics: nucleotide has 3 parts (phosphate group, pentose sugar, nucleotide),
Examples: DNA, RNA
DNA- double helix (spiral), souble nucleotide chain RNA- single nucleotide chain

Subtopic