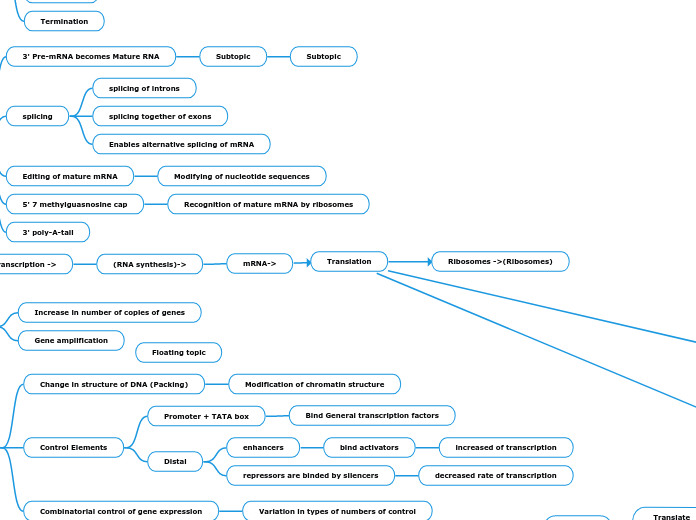
Translation
Involves
Ribosomes
rRNA
Has
2 subunits
Large and Small
3 active sites
Are
A site
Amino acid
E site
Exit site
P site
Growing polypeptide
tRNA
Translate
multiple codons
wobble
effect
Is
Short
clover
shaped
Has
amino acid attached
to 3' end
synthase
anticodon
Includes
Termination
Stop codon is reached
Elongation
Movement of tRNA
from A site to P site
the polypeptide
chain grows
Initiation
Start codon
(AUG)
tRNA
Amino acid
Transcription
Stages of Transcription
Initiation
Acomplished by RNA polymerase
RNA polymerase (RNAP)- Prokaryotes
RNA polymerase II- pre mRNA - EUkaryotes
Elongation
Termination
Transcription level
3' Pre-mRNA becomes Mature RNA
Subtopic
Subtopic
spilcing
splicing of introns
splicing together of exons
Enables alternative splicing of mRNA
Editing of mature mRNA
Modifying of nucleotide sequences
5' 7 methylguasnosine cap
Recognition of mature mRNA by ribosomes
3' poly-A-tail
DNA ->
Transcription ->
(RNA synthesis)->
mRNA->
Level of Genetic Code
Increase in number of copies of genes
Gene amplification
Transcription Elements
Change in structure of DNA (Packing)
Modification of chromatin structure
Control Elements
Promoter + TATA box
Bind General transcription factors
Distal
enhancers
bind activators
increased of transcription
repressors are binded by silencers
decreased rate of transcription
Combinatorial control of gene expression
Variation in types of numbers of control
elements and specific transcription factors
Coordinately controlled genes
Eukaryotic form of operon model
Structure of DNA
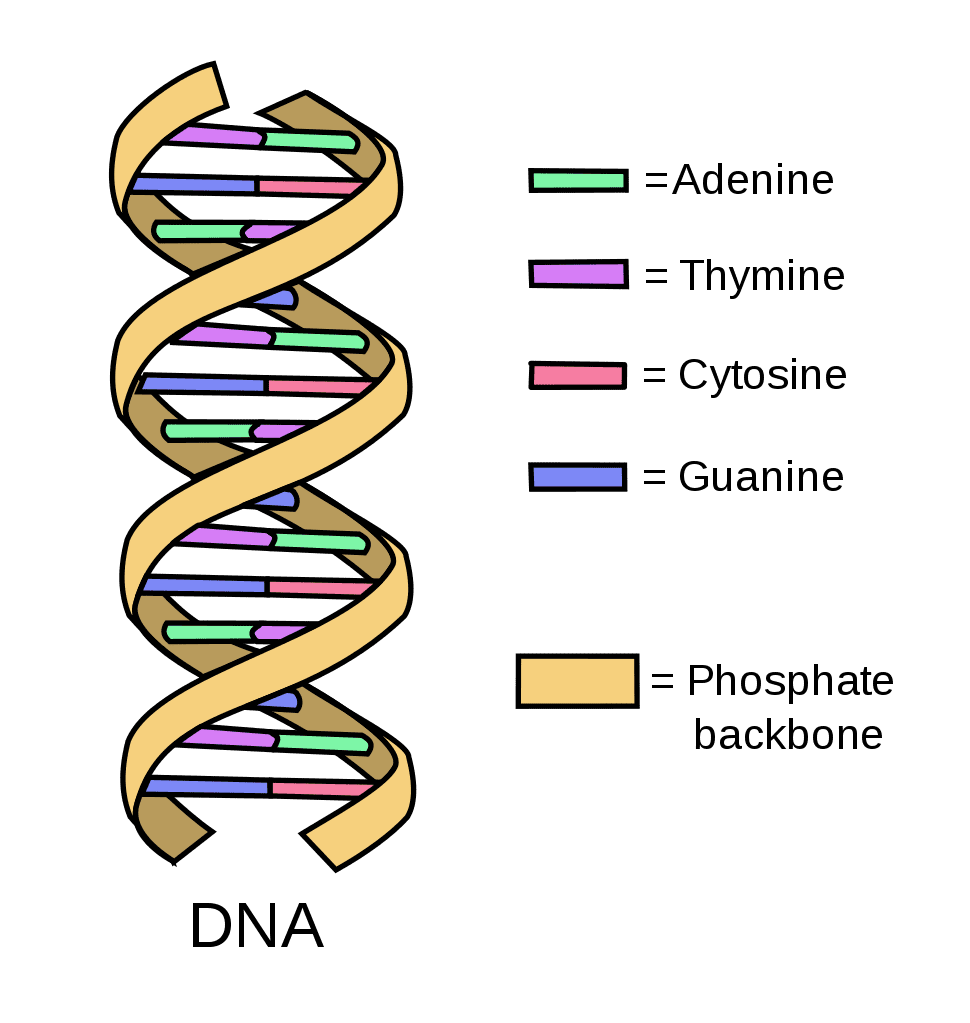
DNA

Nucleotides
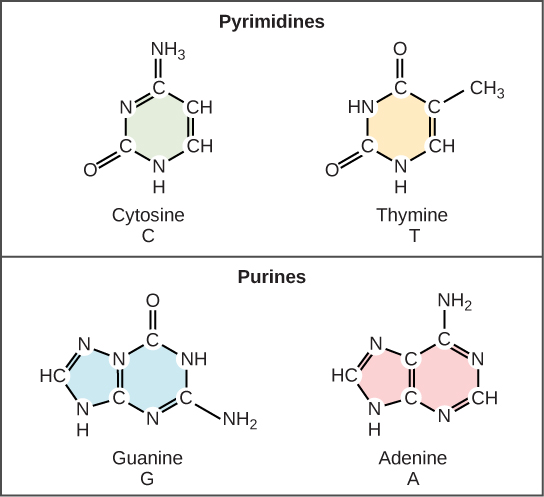
Base
Cytosine
Guanine
Thymine
Adenine

Pentose Sugar (Deoxyribose