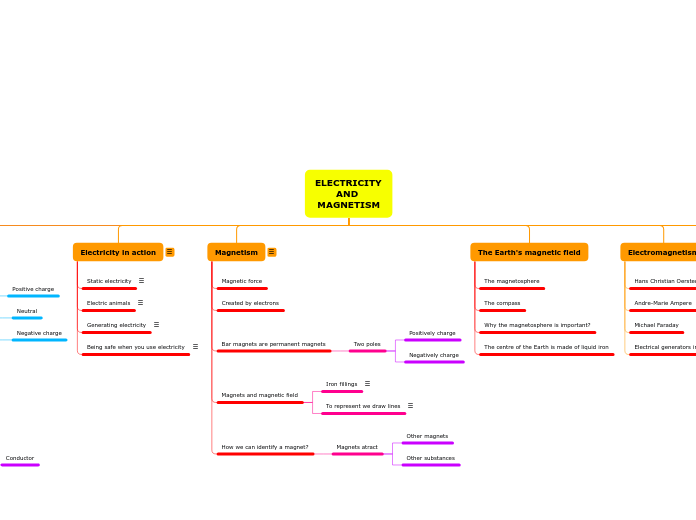
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
Electricity
Atoms
Nucleus
Protons
Positive charge
Neutrons
Neutral
Electrons
Negative charge
Electryc current
Positive
Negative
Electryc circuits
Switch
Battery
Two terminals
Conductor
Electricity in action
Static electricity
Electric animals
Generating electricity
Being safe when you use electricity
Magnetism
Magnetic force
Created by electrons
Bar magnets are permanent magnets
Two poles
Positively charge
Negatively charge
Magnets and magnetic field
Iron fillings
To represent we draw lines
How we can identify a magnet?
Magnets atract
Other magnets
Other substances
The Earth's magnetic field
The magnetosphere
The compass
Why the magnetosphere is important?
The centre of the Earth is made of liquid iron
Electromagnetism
Hans Christian Oersted
Andre-Marie Ampere
Michael Faraday
Electrical generators in power stations
Electromagnets
Maglev
Electric bell
Speakers and microphones